Change In Gibbs Free Energy Graph
$\endgroup$ – Gert Aug 16 '15 at 16:42.

Change in gibbs free energy graph. Anyway, by playing with the numbers a bit in the above equation, you can show yourself that the free energy of mixing is most negative when the. The best way to think about the process is via a curve. It is an extensive function like the internal energy E , entropy S , and Helmholtz free energy A.
LatexG = H\;-\;TS/latex Free energy is a state function, and at constant temperature and pressure, the standard free energy change (Δ G °) may be expressed as the. Adding to the confusion is the occasional use of Gibbs potential in place of Gibbs energy or Gibbs free energy, even when it refers to the Gibbs free energy of an. Δ G = Δ H − T Δ S.
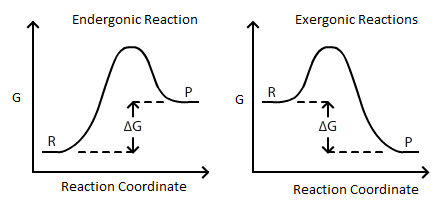
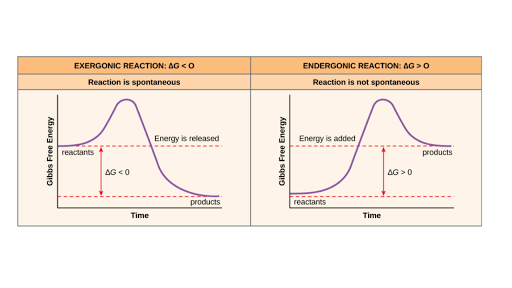
Meanwhile, the equilibrium state of an endergonic reaction in, the Gibbs energy of the products is higher than that of the reactants. Going from which initial state to which final state?. The standard Gibbs free energy of formation (G f °) of a compound is the change of Gibbs free energy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their standard states (the most stable form of the element at 1 bar of pressure and the specified temperature, usually 298.15 K or 25 °C).
Get 1:1 help now from expert Chemistry tutors. G = H – T S (4-1). Generally, all reactions want to go to a lower energy state, thus a negative change is favored.
The enthalpy and entropy changes of a reaction, together with the temperature at which the reaction takes place. Another way to look at it is that the disorder or randomness of the system increases. (ΔH°, ΔG°, S°) Definitions of standard states:.
These are summarized in the table below. And if we do that, we ultimately get the change in Gibbs-free energy for the overall reaction of A going to C. Summary of Gibbs free energy.
N 2 + 3H 2 → 2NH 3. How does this simple equation encompass the entropy change of the world ΔS total. Made by faculty at the Univer.
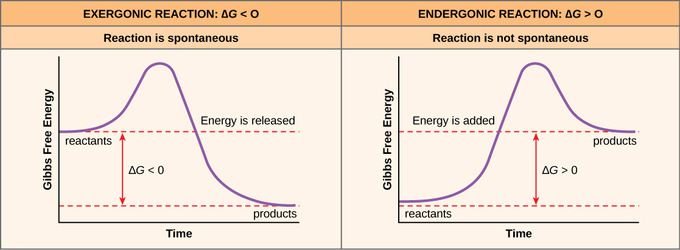
In the case of an exergonic reaction, depicted below, the chart indicates two key things:. So why is Gibbs free energy zero for phase changes at constant temperature and pressure?. Thermodynamically, that is to say that their free energy may increase very fast as one tries to add other components to such a phase.
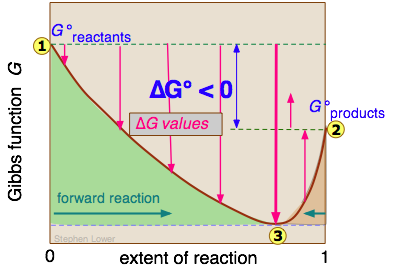
The physical meaning of ΔG Δ G is that it tells us how far the free energy of the system has changed from G° of the pure reactants (point 1). The term 'spontaneity' has a connotation of immediacy in common speech usage. In the Gibbs free energy change equation, the only part we as scientists can control is the temperature.
Remember that the Gibbs free energy of mixing is not a molar quantity and depends on n (unlike the reaction Gibbs free energy). Where ν i is the stoichiometric coefficient (a,b,c,d) for species “i”, and G fi is the free energy of formation per mole of species “i” 1. Next, let's get a Maxwell relation for the Gibbs' Free Energy.
ΔG° = ΔH° - TΔS°. Ron Rusay" A Reaction Coordinate (Energy) Diagram Thermodynamic Quantities Gibbs standard free energy change (ΔGo) Enthalphy (ΔHo):. A measure of freedom of motion ΔGo = ΔHo - TΔSo ΔG,ΔH,ΔS, ΔE are state.
Gibbs Free Energy Change, ∆G Gibbs free energy is a term that combines the effect of enthalpy and entropy into one number The balance between entropy and enthalpy determines the feasibility of a reaction. The Gibbs free energy (also known as the Gibbs function) is defined as. We have an equation.
In the equilibrium state of an exergonic reaction, the Gibbs energy of the products is lower than that of the reactants. O K«o OK= 0 O K>1 OK. Gibbs free energy, denoted G, combines enthalpy and entropy into a single value.
The term standard state is used to describe a reference state for substances, and is a help in thermodynamical calculations (as enthalpy, entropy and Gibbs free energy calculations). The Gibbs free energy is also known as the free energy, the Gibbs function, or available energy. So instead, we can add together the individual change in Gibbs-free energy for each step, because remember Gibbs-free energy is a state function.
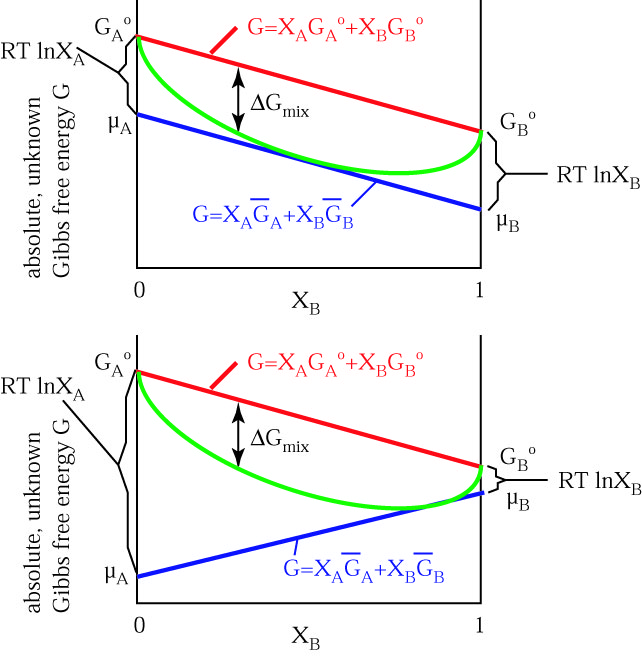
As a function of composition, the gibbs free energy for the combination of pure A and pure B is a straight line connecting g. The free energy of the system decreases. However, a change in Gibbs free energy (∆G) accompanying a process can be measured accurately.
The change in entropy (S) increases. For a gas, the standard state is as a pure gaseous substance as a. As the reaction moves from 100% A to 50% A/50% B, the Gibbs energy falls to a minimum.
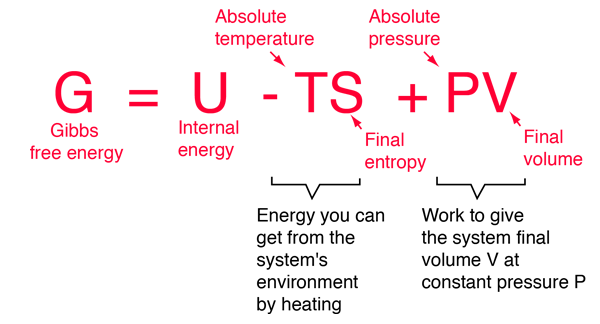
ΔG = -81.5KJ – (298 K) (-0.10KJ/K) ΔG = -24.7KJ. In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that can be used to calculate the maximum of reversible work that may be performed by a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure.The Gibbs free energy (= −, measured in joules in SI) is the maximum amount of non-expansion work that can be extracted from a thermodynamically closed system (can exchange. G = H - T S.
Finally, the change in Gibbs free energy is zero (ΔG=0) for a reaction that has reached equilibrium. When the entropy of the universe increases it means that the Gibbs Free Energy of the system decreases. Equation for Gibbs free energy is:.
Standard Free Energy Change, D G o —the standard free energy change, D G o can be calculated (1) by substituting standard enthalpies and entropies of reaction and a Kelvin temperature into the Gibbs equation or (2) by combining standard free energies of formation through the expression. The Ellingham diagram plots the Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) for each oxidation reaction as a function of temperature. (1) the difference between the free energy of the reactants and products is negative and (2) the progress of the reaction requires some input of free energy (shown as an energy hill).
In Figure 8.9, the energetic coupling of ATP hydrolysis and an endergonic reaction are shown. Likewise the change in Gibbs free energy is positive (ΔG>0) for a nonspontaneous process and requires the input of free energy from the surroundings. The intensive Gibbs free energy of a phase is also, in general, a function of composition.
Standard Heats and Free Energies of Formation and Absolute Entropies of Elements and Inorganic Compounds. Question 3 (1 point) Which graph shows the change in Gibbs Free Energy for the reaction A the equilibrium constant K = 0.33?. Describes how Gibbs free energy depends on pressure and temperature to give insight on how fugacity depends on these variables.
When ΔG is less than zero, there is a thermodynamic driving force for the reaction or process in the forward direction (as written). One of the reasons for this is the widespread use of molar Gibbs free energy, partial molar Gibbs free energy, or simply Gibbs energy or Gibbs free energy but with the unit of J/mol. Since the arrow is pointing towards temperature AND coming from the side opposite to #G#, #S# is negative.
B if SOKA 10% SORB SOKA 30%A 50MB 0000. The enthalpy ( ∆H) is a measure of the actual energy that is liberated when the reaction occurs (the “heat of reaction”). For any process to be possible, the change in Gibbs' free energy must be negative.
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS. The heat given off or absorbed during a reaction Entropy (ΔSo):. Summary of Gibbs Free Energy.
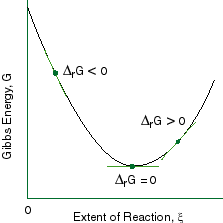
Graph of G(T,p)=f(ξ) G (T, p) = f (ξ). This is a spontaneous process. Question 19 5 Pts The Graph Of Gibbs Free Energy Versus Reaction Coordinate (and The Composition Of The System) For The Reaction A=B Is Shown To The Right.
If it is negative, then the reaction gives off energy, while if it is positive the reaction requires energy. Such a Gibbs potential is depicted in the figure. This graph can be used to determine the equilibrium constant and to predict the direction of change.
$\Delta G$ is a state function. The superscript degree symbol (°) indicates that substances are in their standard states. MS15a, Gibbs Free Energy and Phase Diagrams 11/00.
The change in the standard Gibbs Free Energy (G) of an exergonic reaction is negative (less than 0). The change in Gibbs Free Energy (ΔG) for any process is related to changes in enthalpy (ΔH) and entropy (ΔS) by the relationship ΔG = ΔH - TΔS where T is absolute temperature in Kelvins. If ∆G r < 0, (i.e., ∆G r is negative and thus G r decreases as the reaction proceeds), then the reaction proceeds spontaneously as written 2.
$\Delta G^o$ gives you thermodynamic favorability of a reaction under standard conditions (Q=1) and even reactions with positive values of $\Delta G^o$ (unfavored under standard conditions) can be driven to proceed if the concentrations of the reactants and products are made extreme enough. Your interpretation of the equation is correct. In fact, under the conditions that a reaction is in a state of dynamic equilibrium, ΔG (as opposed to the free energy change under standard conditions, ΔG°) is zero.
When a system changes from a well-defined initial state to a well-defined final state, during a reversible transformation, the Gibbs free energy equals the work exchanged. In which S refers to the entropy of the system.Since H, T and S are all state functions, so is G.Thus for any change in state, we can write the extremely important relation. Where ∆H is the enthalpy, T is absolute temperature, and ∆S is entropy.
Some of the ice polymorphs. It is easy as long as you remember to convert the entropy change value into kJ. The Gibbs free energy graph shows whether or not a reaction is spontaneous-- whether it is exergonic or endergonic.
100% A 100% B Reaction Coordinate What Is The Equilibrium Constant For The Forward Reaction A=B?. O A, as it is equivalent to the chemical potential of the pure element. ΔH° = -0.4 kJ mol -1.
If ∆G r > 0. All real phases have some range of variability in composition, though some are always nearly pure. The change in the Gibbs free energy of the system that occurs during a reaction is therefore equal to the change in the enthalpy of the system minus the change in the product of the temperature times the entropy of the system.
This is given by the relationship :. GIBBS FREE ENERGY VS. Gibbs free energy (G) is also known as free energy or Gibbs energy.
Structural Biochemistry/Enzyme/Gibbs free energy graph. The molar gibbs free energy of a pure element is often give the symbol µ. $\begingroup$ The change in Gibbs Free Energy for which transformative process?.
Determine the standard free energy change for the following reaction at 25 o C. The Gibbs free energy is a particularly important function in the study of phases and phase transitions. However, if some system's variable changes other parameters might not necessarily adapt to these changes and the system might not always immediately assume the point of lowest possible Gibbs free energy.
Exergonic reactions occur spontaneously (no outside energy is required to start. The sign of the change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG) for a chemical reaction tells us if the reaction is spontaneous or not:. Now one fun way that I kind of remember the state function like quality of delta G, as.
For example if you supercool liquid water to -10 degrees C, let the water freeze and do this in a way that the final state is solid water at -10 degrees C, the change in Gibbs free energy will be negative. {ΔG} = {ΔH}− {TΔS} ΔG = ΔH −T ΔS. This new property is called the Gibbs free energy change (G) (or simply the free energy), and it is defined in terms of a system’s enthalpy and entropy as the following:.
Entropy IS a natural variable, which is why it said to not be changing in this case. If we have mixtures that have more B than A, then the Gibbs energy is higher than the minimum. ∆G = ∆H - T∆Ssystem For any spontaneous change, ∆G will be negative.
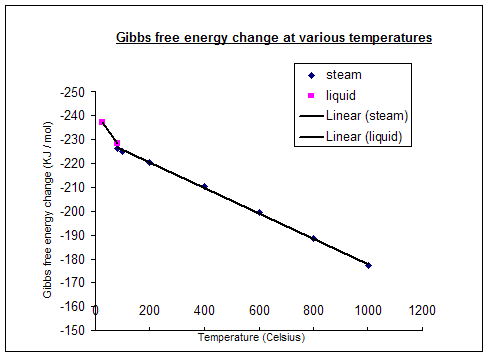
Substitute the above values in this equation. Exergonic and endergonic reactions are characterized by changes in Gibbs energy. We have seen how we can calculate the standard change in Gibbs free energy, ΔG⁰, but not all reactions we are interested in occur at exactly 298 K.The temperature plays an important role in determining the Gibbs free energy and spontaneity of a reaction.
Negative ΔG indicates that the reaction is exergonic and spontaneous. Also, the Gibbs free energy of mixing is defined relative to pure A and B. Gibbs free energy (G) can be defined by combining the enthalpy (H), entropy (S), along with the Kelvin temperature (T) as shown in the following equation, G = H – TS.
ΔG can predict the direction of the chemical reaction under two conditions:. The change in G for a reversible, isothermal change of state is given by. Given ΔH and S are -81.5KJ and -1.0J/K.
The change in free energy, ΔG, is equal to the sum of the enthalpy plus the product of the temperature and entropy of the system. The Gibbs free energy, G, is the maximum amount of nonexpansion work that can be extracted from a closed system, and can be attained only in a completely reversible process. In a practical and frequently used form of Gibbs free energy change equation, Δ G is calculated from a set values that can be measured by scientists:.
ΔG° = -0.4 - 298 (-0.2442) = -817.6 kJ mol -1. The unit of Gibbs free energy is joules/mole (or calories/ mole). Effect of Temperature on Gibbs Free Energy and Spontaneity of Reactions Chemistry Tutorial Key Concepts.
G = H - (TS) If the reaction is run at constant temperature, this equation can be written as follows. It is important to realise that we are talking about standard free energy change here - NOT the free energy change at whatever temperature the reaction was carried out. Nonstandard state free energy change:.
The behavior of \(G(N, P,T)\), particularly as a function of \(P\) and \(T\), can signify a phase transition and can tell us some of the thermodynamic properties of different phases. Change in G r can be calculated as:. So if you had to calculate the Gibbs free energy change at, say, 298 K, you can just slot the numbers in:.
In this screencast, John Holman explains the variation of Gibbs Energy change with temperature. ΔG is the change in free energy. ΔG = ΔH – TΔS.
ΔG = ΔH – T ΔS (4-2) Must know this!. If the hydrolysis of ATP releases 7.3 kcal of free energy, use the graph in this figure to estimate what you would expect the ∆G values to be for the uncoupled reaction and the two steps in the coupled reaction. Instead the system might "get stuck" in some local minimum of the Gibbs potential.
ENTROPY, TEMPERATURE, VOLUME, AND PRESSURE. This type of graph is called a reaction coordinate diagram. A single reaction can have an infinite number of ΔG Δ G values.

Schematic Representation Of The Gibbs Free Energy Curve Vs Temperature Download Scientific Diagram
Free Energy The School Of Biomedical Sciences Wiki

Thermodynamics Of Phase Diagrams
Change In Gibbs Free Energy Graph のギャラリー

Homogeneous Nucleation Tec Science
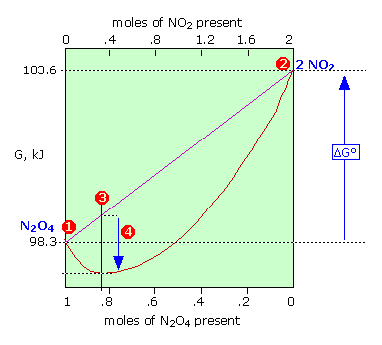
Free Energy And Equilibrium Chemistry Libretexts
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsj Qnkqsf2tg79dukhs8xq Y7ebfqn8mckusqlghqcxclr4l9c Usqp Cau
Http Www Physics Uwo Ca Lgonchar Courses P96 Lecture1 Intro Thermodynamics Pdf

7 First Order Phase Transitions
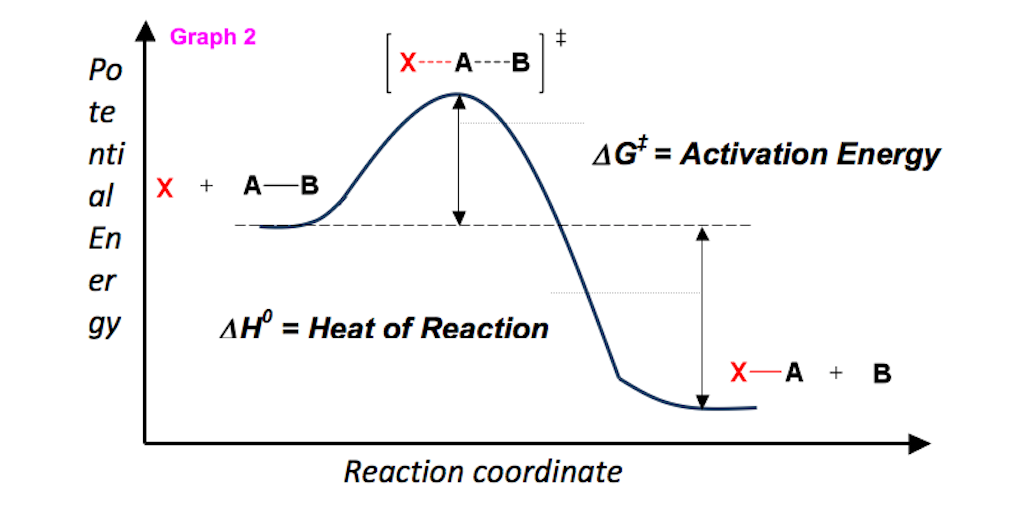
Energy Diagram Module Series Part Two Gibbs Free Energy And Spontaneity Organic Chemistry Help
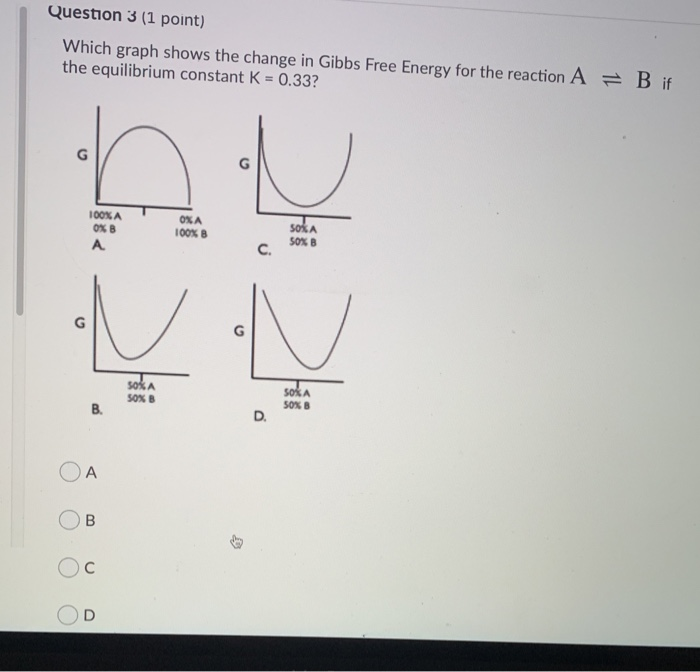
Solved Question 3 1 Point Which Graph Shows The Change Chegg Com

Gibbs Free Energy T P Dependence Youtube

Gibbs Free Energy
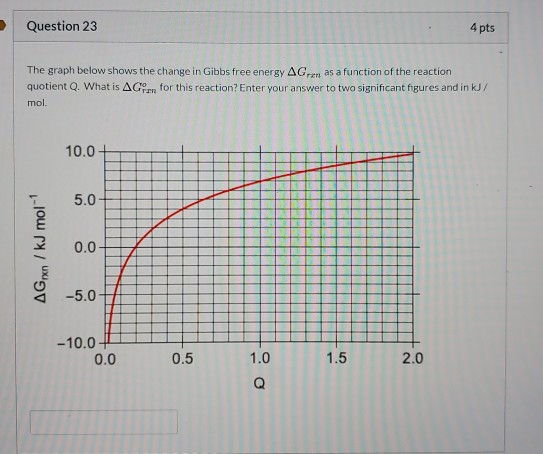
Solved Question 23 4 Pts The Graph Below Shows The Change Chegg Com
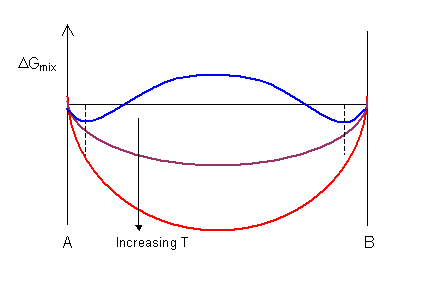
Doitpoms Tlp Library Phase Diagrams And Solidification Free Energy Curves
Gibbs Free Energy Wikipedia

Gibbs Free Energy Of Mixing And Liquid Liquid Separation Youtube

What Do We Mean When We Talk About Gibbs Free Energy Physics Stack Exchange
3
What Is True Of Gibbs Free Energy Changes For Reactions That Proceed Spontaneously

Gibbs Free Energy Wikipedia

The Diagram For The Free Energy Of The Rea Clutch Prep
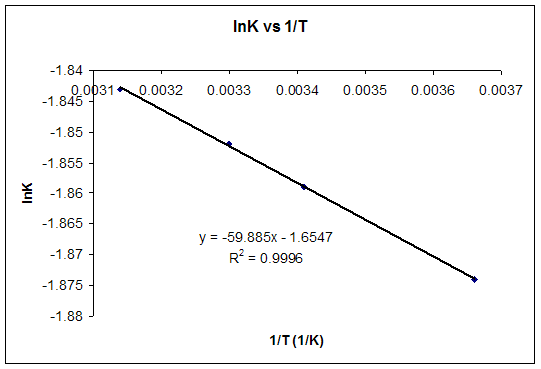
Gibbs Free Energy

9 A Contributions To The Change In Gibbs Free Energy G During The Download Scientific Diagram

Gibbs Free Energy What It Is Equation Conditions Videos And Examples

Ap Class Notes

Schematic Showing The Gibbs Free Energy Of Mixing As A Function Of Download Scientific Diagram
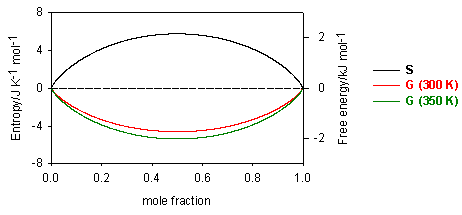
The Thomas Group Ptcl Oxford
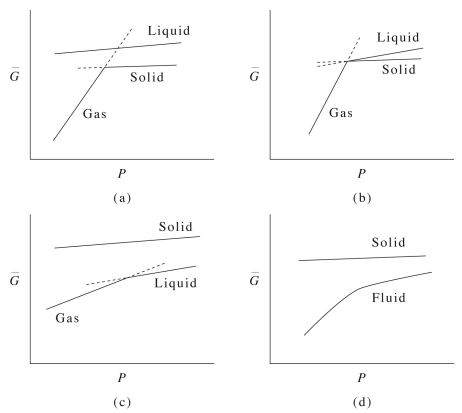
23 2 Gibbs Energies And Phase Diagrams Chemistry Libretexts

Gibbs Free Energy Boundless Chemistry

Reaction Quotient And Gibbs Free Energy At The Start Of A Reaction Chemistry Stack Exchange
Structural Biochemistry Enzyme Gibbs Free Energy Graph Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World

Gibbs Free Energy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Www Victorjtemple Com Enzymes overview ppp 3 Pdf
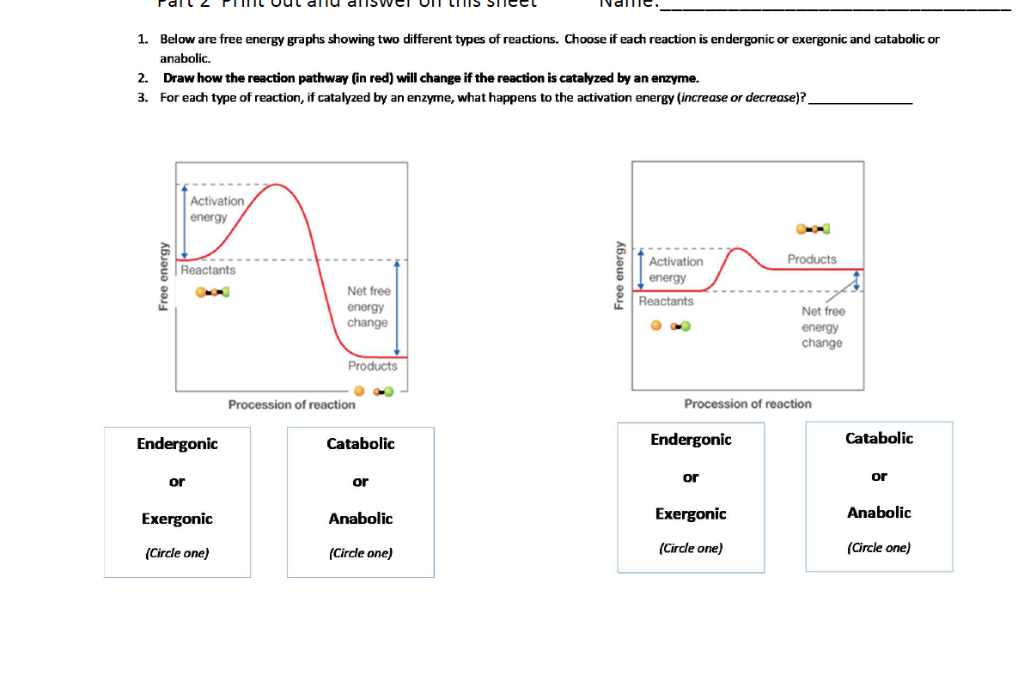
Solved 1 Below Are Free Energy Graphs Showing Two Differ Chegg Com
Q Tbn 3aand9gcserbo9ydtztveufbzitzcg1ikeqajbuumqyssx I1ewqqesjua Usqp Cau
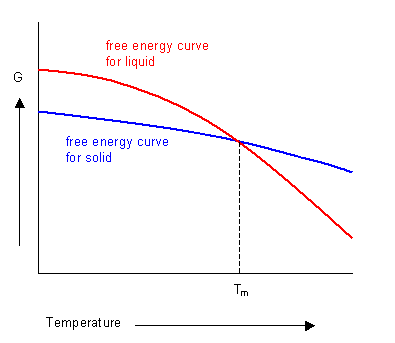
Doitpoms Tlp Library Phase Diagrams And Solidification Free Energy Curves
Q Tbn 3aand9gct4jnn8a5ik1licws2ndnioo0tss9jeatj4eobftvq Xpudf9 Usqp Cau

Reaction Energy Concepts
Connection Between E Cell G And K Chemistry Libretexts

7 First Order Phase Transitions

Gibbs Free Energy Changes Equation Calculations Reaction Feasibility Extraction Of Metals Cell Emf Gce A Level Chemistry Revision Notes
Doitpoms Tlp Library Fuel Cells Efficiency And Reaction Conditions
Chapter 9 Lecture Notes

Gibbs Free Energy Boundless Chemistry

Gibbs Free Energy Changes Equation Calculations Reaction Feasibility Extraction Of Metals Cell Emf Gce A Level Chemistry Revision Notes
Helmholtz And Gibbs Free Energies

16 4 Free Energy Free Energy Chemistry Textbook Thermodynamics
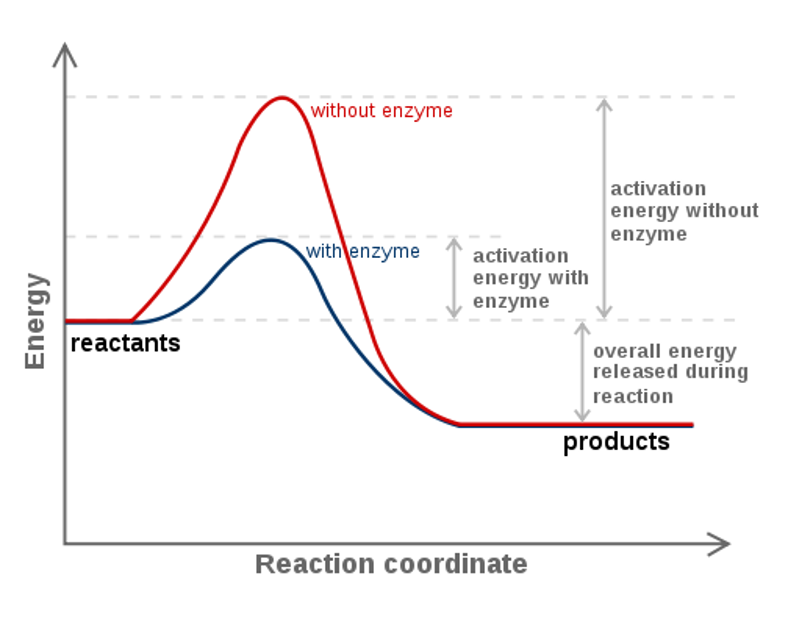
Ch103 Chapter 7 Chemical Reactions In Biological Systems Chemistry
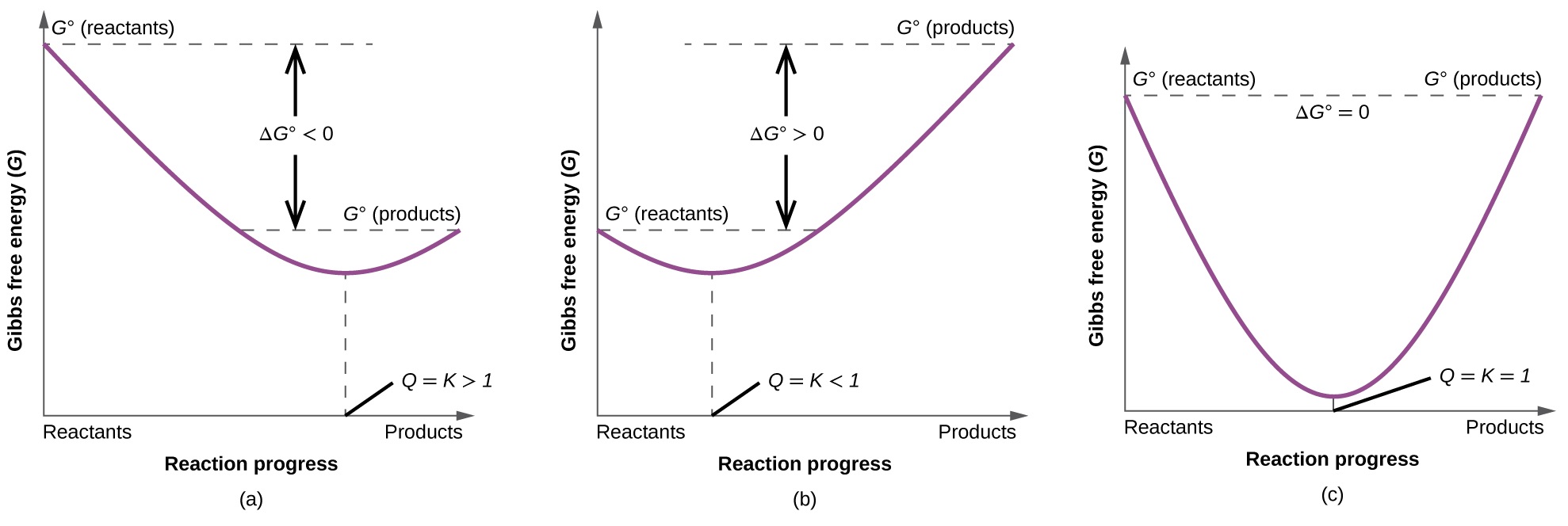
16 4 Gibbs Energy Chemistry Libretexts

Gibbs Free Energy Of Activation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
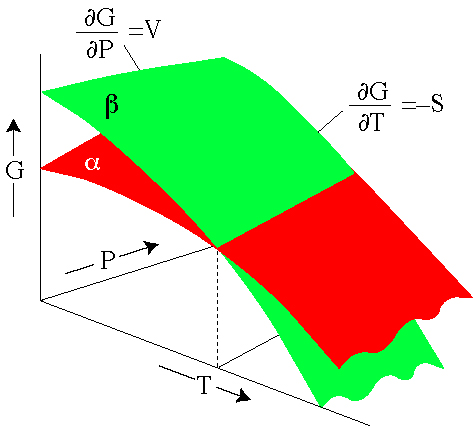
Gibbs Energy

Gibb S Free Energy And The Nature Of Chemical Reactions

The Diagram For The Free Energy Of The Rea Clutch Prep
The Gibbs Free Energy Of A Reacting Mixture And The Equilibrium Composition

Solved 1 Points Calculate The Standard Change In Gi Chegg Com

Thermodynamics What Is An Intuitive Explanation Of Gibbs Free Energy Quora

The Diagram Shows The Free Energy Change O Clutch Prep
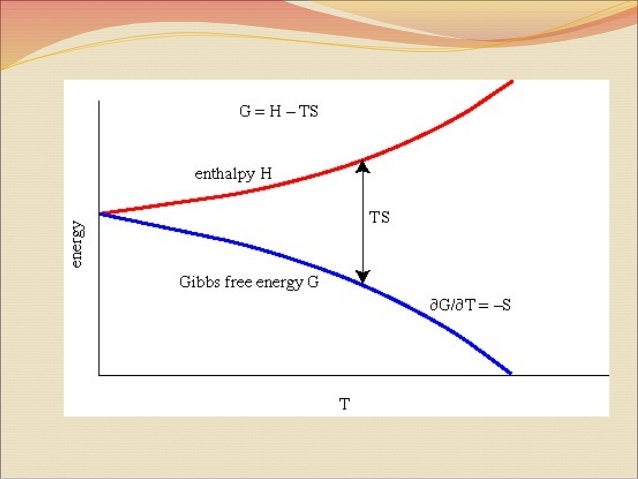
Plotting Of Different Parameters Entropy Enthalpy Gibbs Free Energy

Schematic Graph Of The Free Energy Vs Mole Fraction Of Solute For Download Scientific Diagram

Gibbs Free Energy Introduction Video Khan Academy

Gibbs Free Energy Change Dg And Entropy Change Ds Secondary Science 4 All

Mcat Diagram Quizlet
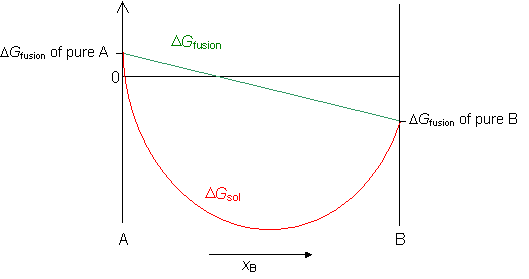
Doitpoms Tlp Library Phase Diagrams And Solidification Free Energy Curves

Gibb S Free Energy And The Nature Of Chemical Reactions

Gibbs Free Energy Wikipedia

The Behavior Of G During A Phase Change

6 2 Potential Kinetic Free And Activation Energy Texas Gateway
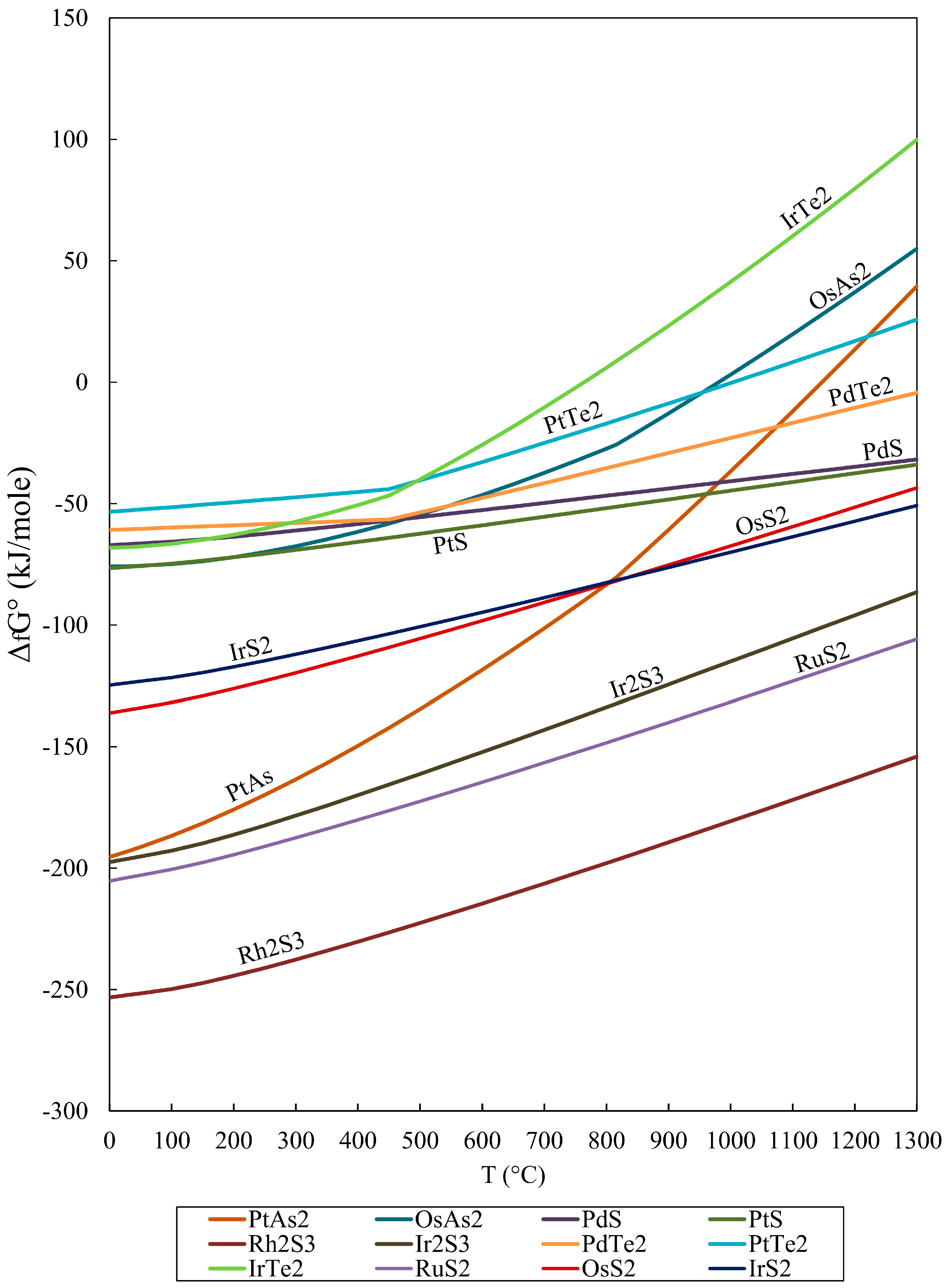
Geosciences Free Full Text Gibbs Free Energy Of Formation For Selected Platinum Group Minerals Pgm Html

Gibbs Free Energy Change Dg And Entropy Change Ds Secondary Science 4 All

7 First Order Phase Transitions
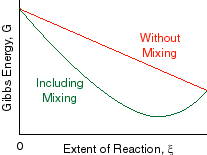
Chapter 9 Lecture Notes
Free Energy Endergonic Vs Exergonic Reactions Article Khan Academy
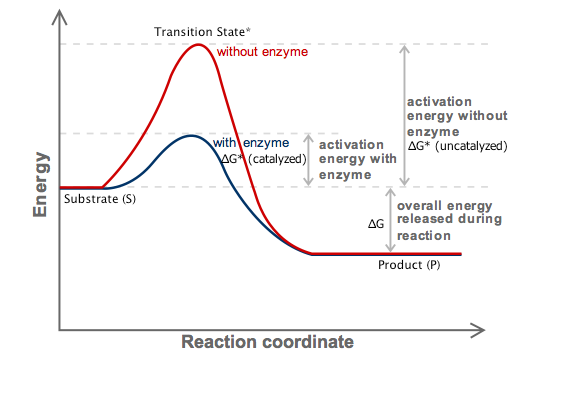
How Do Enzymes Affect Gibbs Free Energy Socratic
Http Www Soest Hawaii Edu Oceanography Courses Ocn623 Spring13 Chemical Equilibrium 13 Handouts Pdf

Calculating Dg At The Extremes Of Reaction Extent Chemistry Stack Exchange
Thermodynamics Notes

Gibbs Free Energy Changes Equation Calculations Reaction Feasibility Extraction Of Metals Cell Emf Gce A Level Chemistry Revision Notes
Graph A Plots Changes In Potential De And Graph B Plots Change In Download Scientific Diagram

What Is An Exothermic Change Quora
Equilibrium Constant
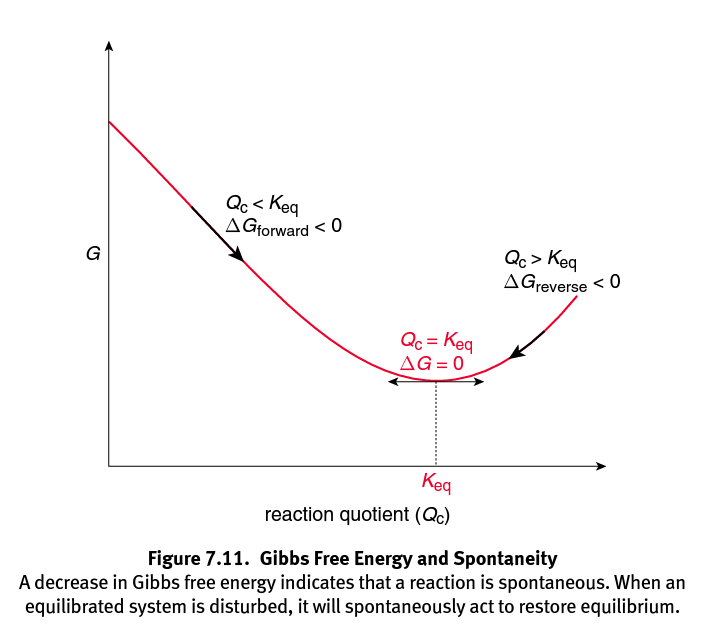
Mcat General Chemistry Chapter 7 Thermochemistry Flashcards Memorang

Gibbs Free Energy Pressure Dependence Youtube
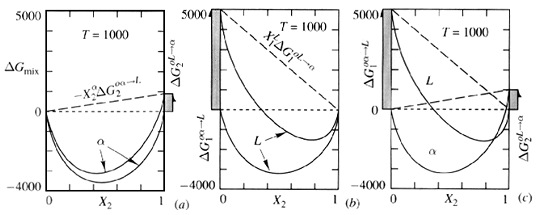
Thermodynamics Of Phase Diagrams
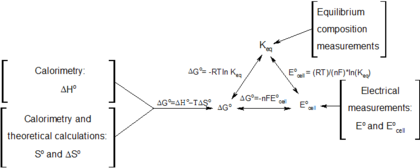
Gibbs Free Energy Wikipedia
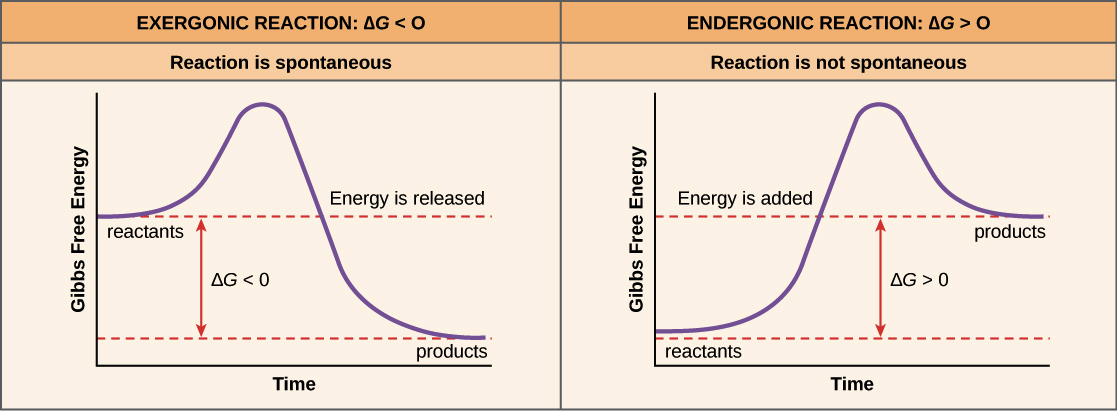
Free Energy Endergonic Vs Exergonic Reactions Article Khan Academy

2 10 Use Of Gibbs Free Energy Phase Transitions
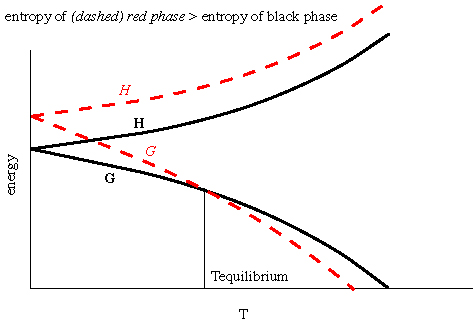
Thermodynamics Notes
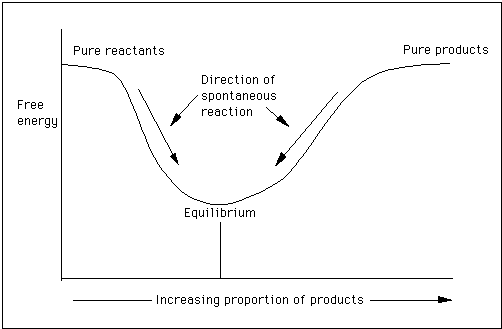
Chemical Thermodynamics
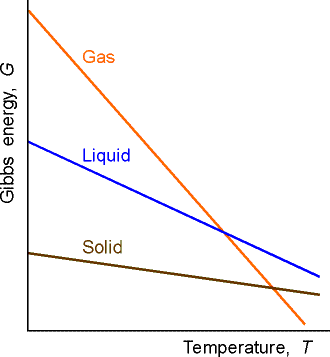
G Props
What Describes The Change In Gibbs Free Energy G Of A Spontaneous Reaction
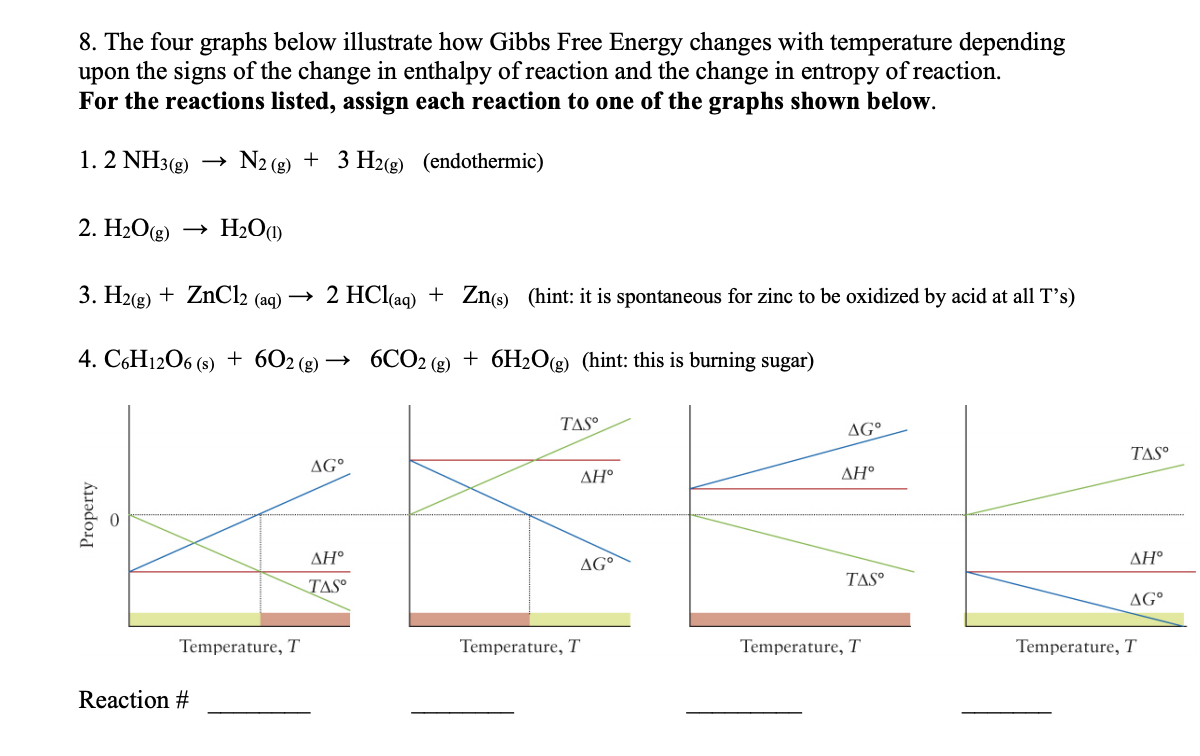
Answered 8 The Four Graphs Below Illustrate How Bartleby
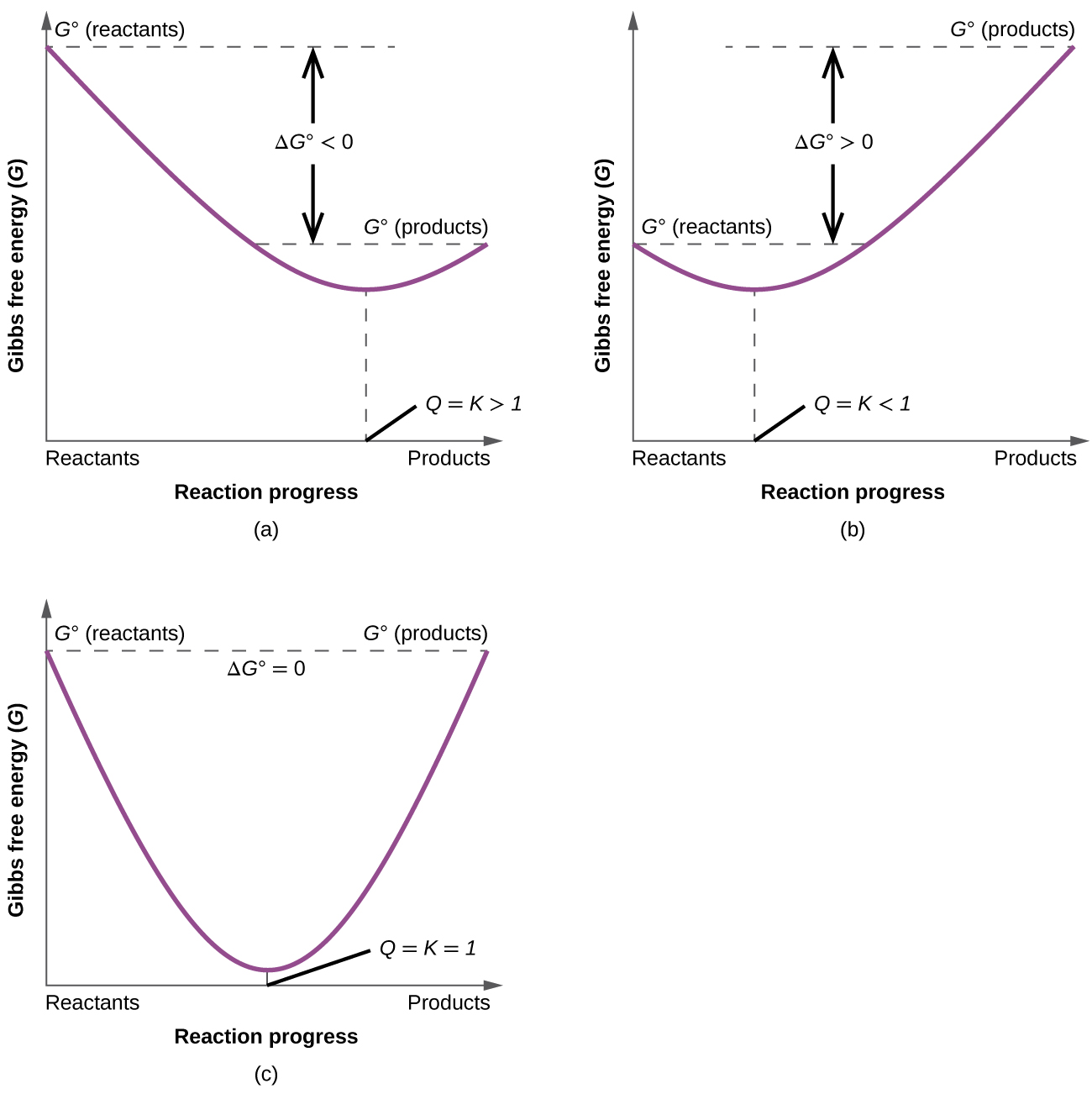
19 6 Gibbs Energy Change And Equilibrium Chemistry Libretexts
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/endergonic-vs-exergonic-609258_final-2904b2c359574dfcb65a9fca2d54179a.png)
Endergonic Vs Exergonic Reactions And Processes

Gibbs Free Energy Changes Equation Calculations Reaction Feasibility Extraction Of Metals Cell Emf Gce A Level Chemistry Revision Notes

Binary Phase Equilibria Tutorial

7 First Order Phase Transitions

Gibbs Energy Change With Temperature Youtube
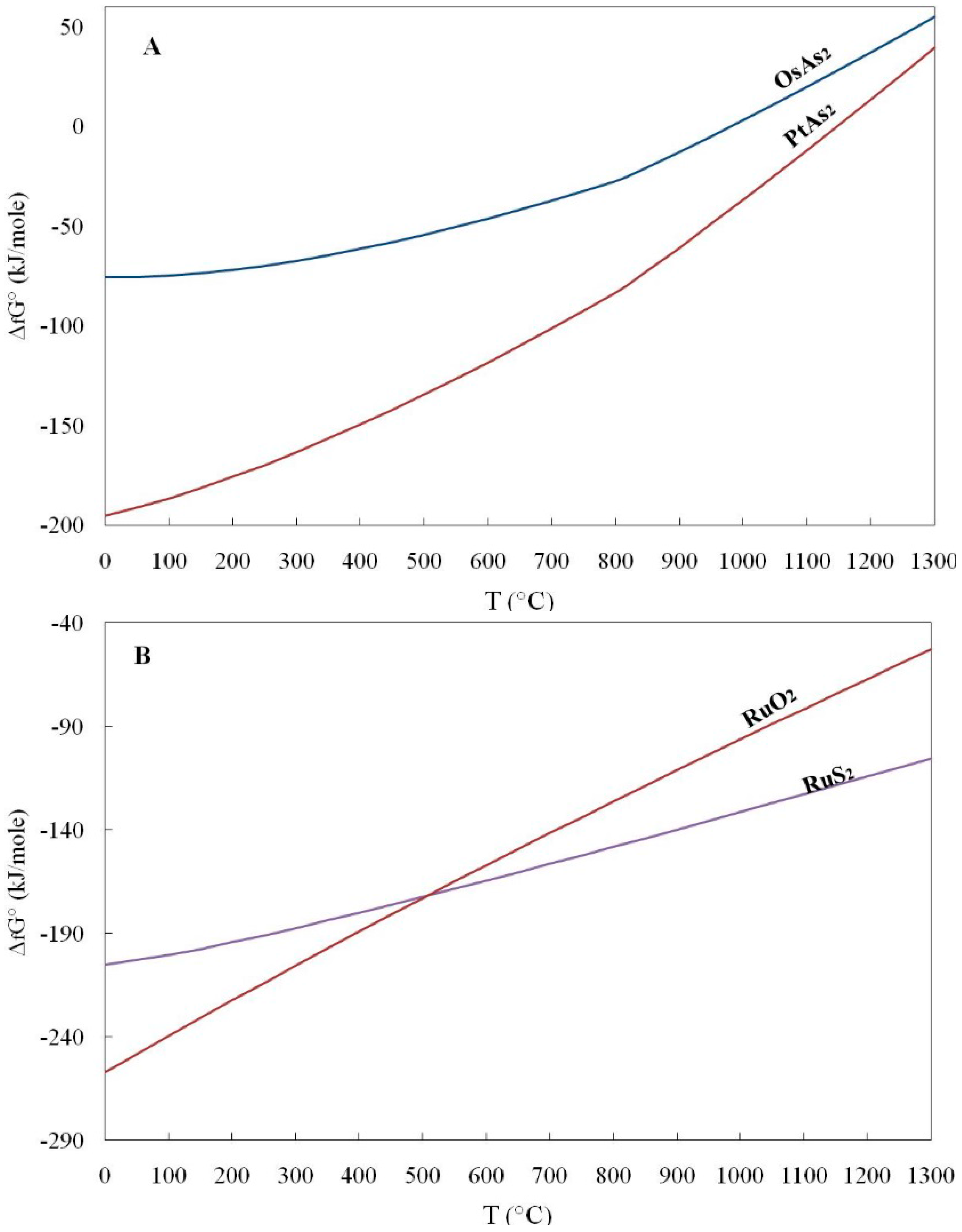
Geosciences Free Full Text Gibbs Free Energy Of Formation For Selected Platinum Group Minerals Pgm Html
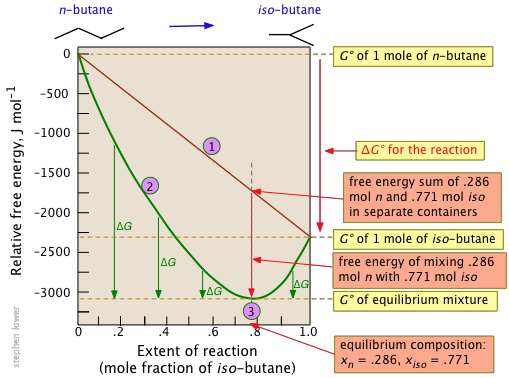
Free Energy And Equilibrium Chemistry Libretexts

Gibbs Free Energy Change Dg And Entropy Change Ds Secondary Science 4 All
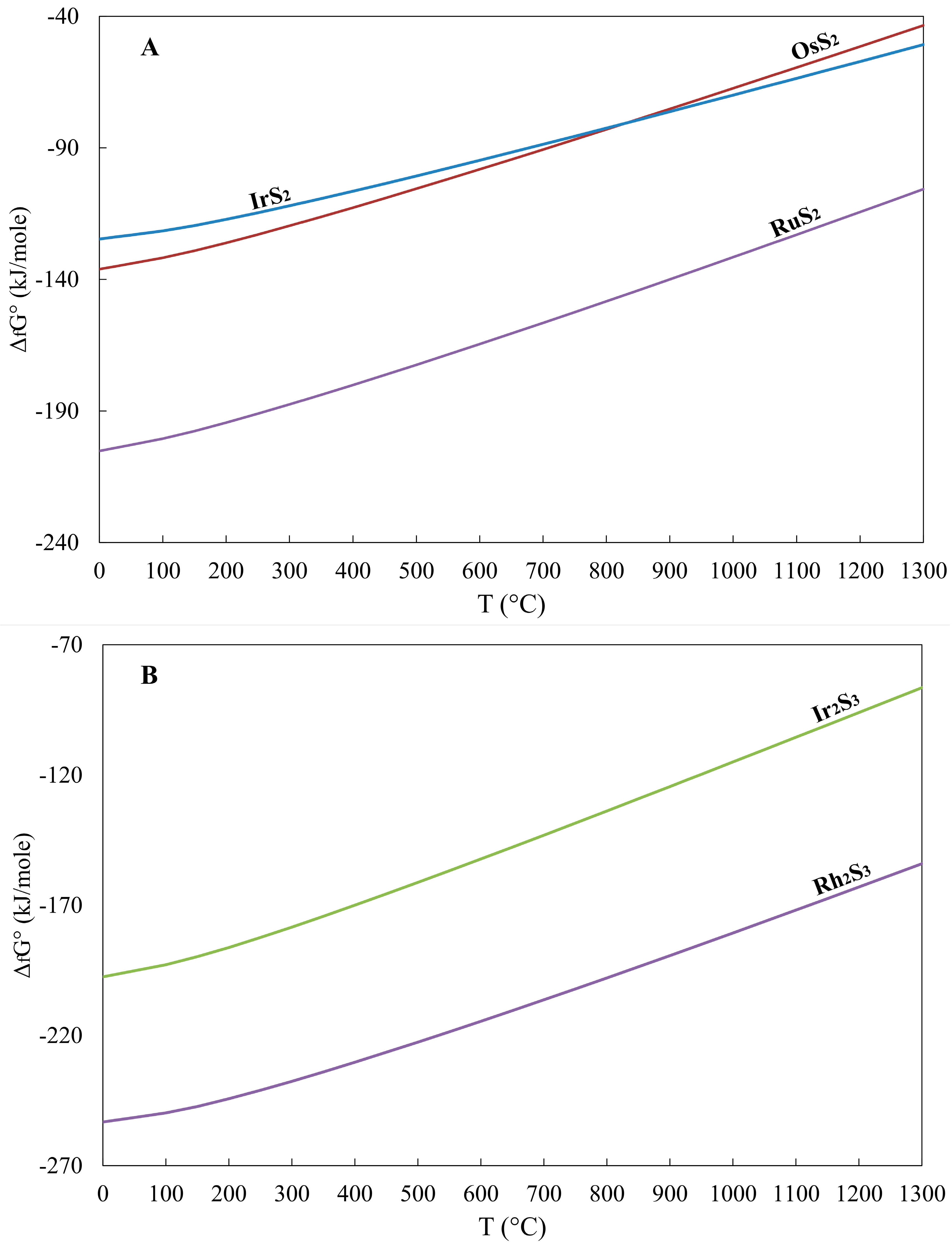
Geosciences Free Full Text Gibbs Free Energy Of Formation For Selected Platinum Group Minerals Pgm Html
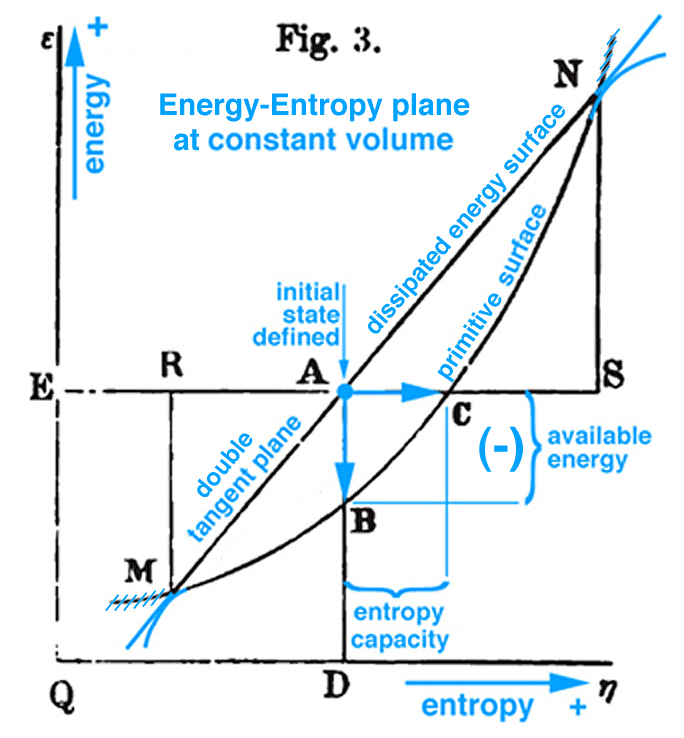
Triple Point Thermodynamic Processes Associated With Gibbs Free Energy
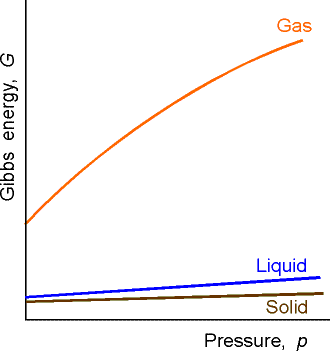
G Props

Gibbs Free Energy Change An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



