Delta G Gibbs Free Energy Equation
298 K, 100 kPa, 1 M of each reactant and product), R, gas constant, T, absolute temperature, ln, natural logarithm, Q r, reaction quotient (unitless),.

Delta g gibbs free energy equation. T = - G/ S At a phase transition delta G = 0. Gibbs free energy, also known as the Gibbs function, Gibbs energy, or free enthalpy, is a quantity that is used to measure the maximum amount of work done in a thermodynamic system when the temperature and pressure are kept constant. The relationship holds true under standard conditions or under non-standard conditions.
It contains plenty of examples and chemistry practice. Cl 2 (g) 0. Cl 2 (aq) 7.
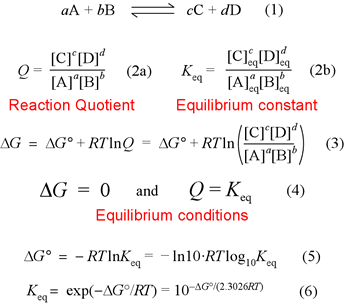
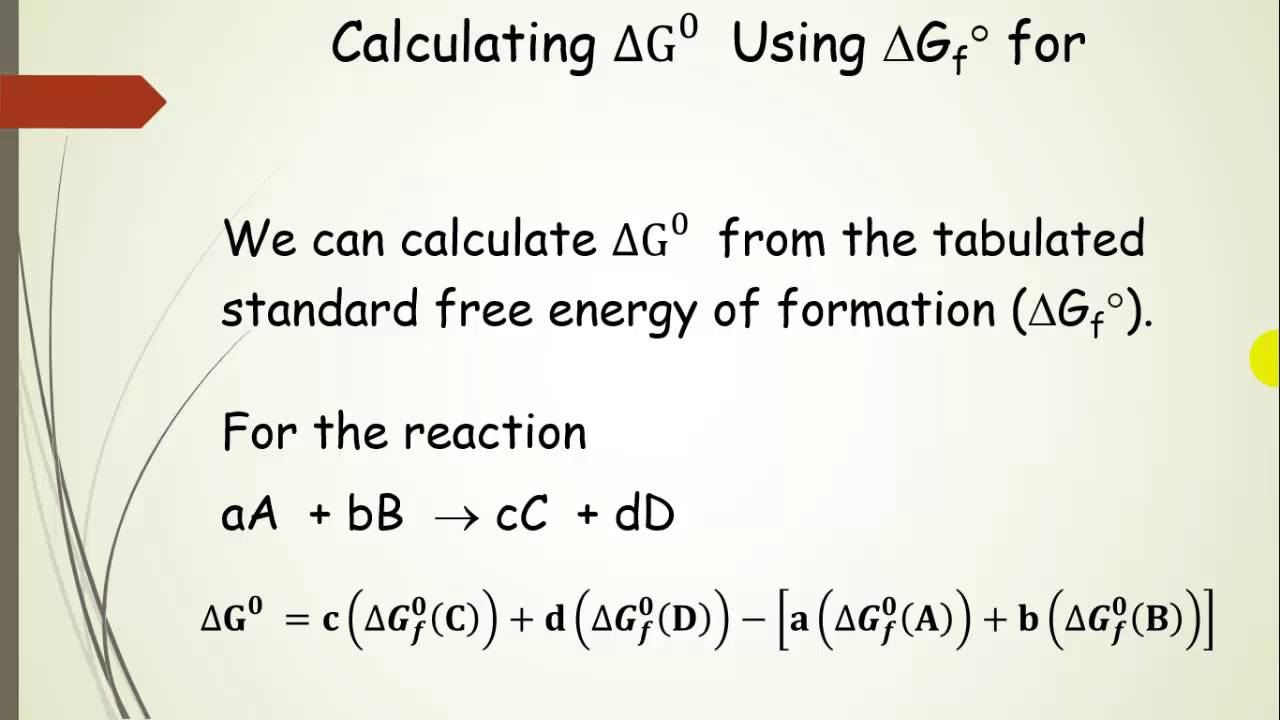
Gibbs free energy is a state function. C 6 H 12 O 6 (s)-910. Recall that for a general reaction of the type aA + bB → cC + dD, the standard free-energy change and the equilibrium constant are related by the following equation:.
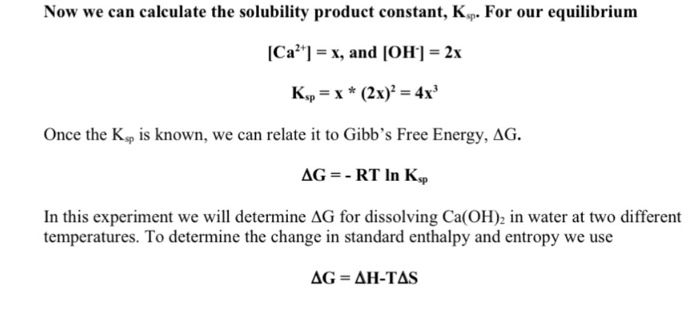
If we examine the Gibbs free energy change equation, we can cluster the components to create two general terms, an enthalpy term, ΔH, and an entropy term, –TΔS. T = (H-G)/ S b. 15 AP Chemistry free response 2c.
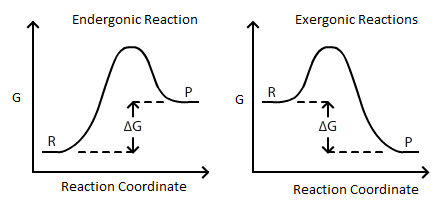
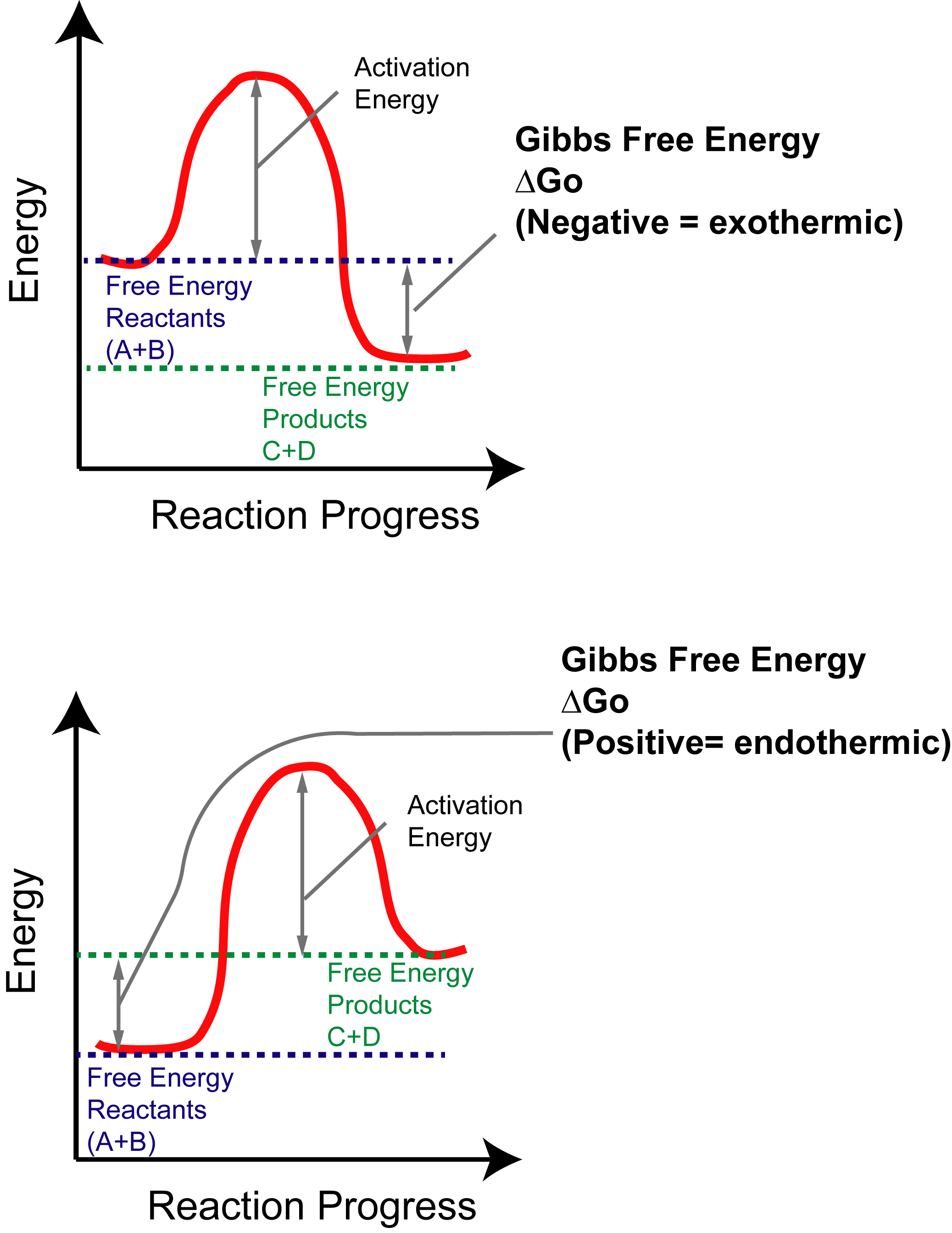
Also known as free enthalpy 1 to distinguish it from Helmholtz free energy) is a thermodynamic potential that can be used to calculate the maximum of reversible work that may be performed by a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure (isothermal, isobaric). ΔG = -81.5KJ – (298 K) (-0.10KJ/K) ΔG. Endergonic reactions consume energy and exergonic reactions release energy.
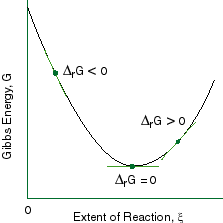
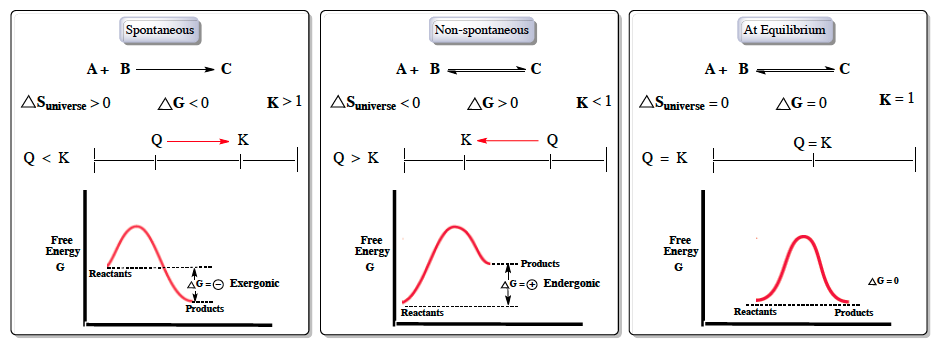
The Gibbs energy is defined for processes that occur at constant pressure and constant temperature. Endergonic reactions have a positive $\Delta G$ and exergonic reactions have a negative $\Delta G$. So we have negative 33.0 kilojoules.
At 25 degrees C delta G zero is negative 33 kilojoules. However, the value of delta G provides no information on the rate of a reaction. It is in between where most life occurs and where we need to use Gibbs free energy to analyze which of the terms win.
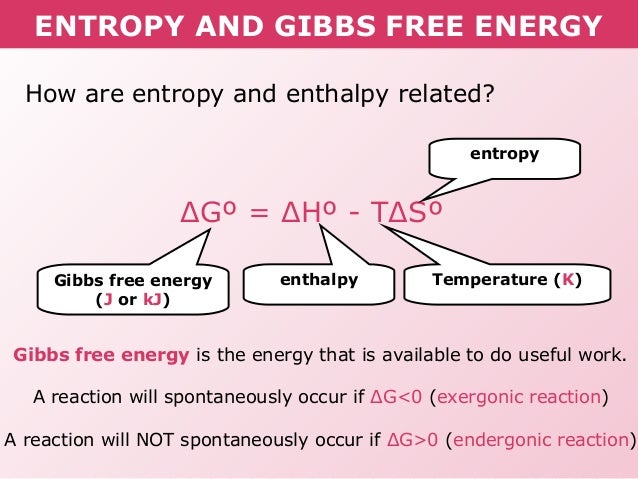
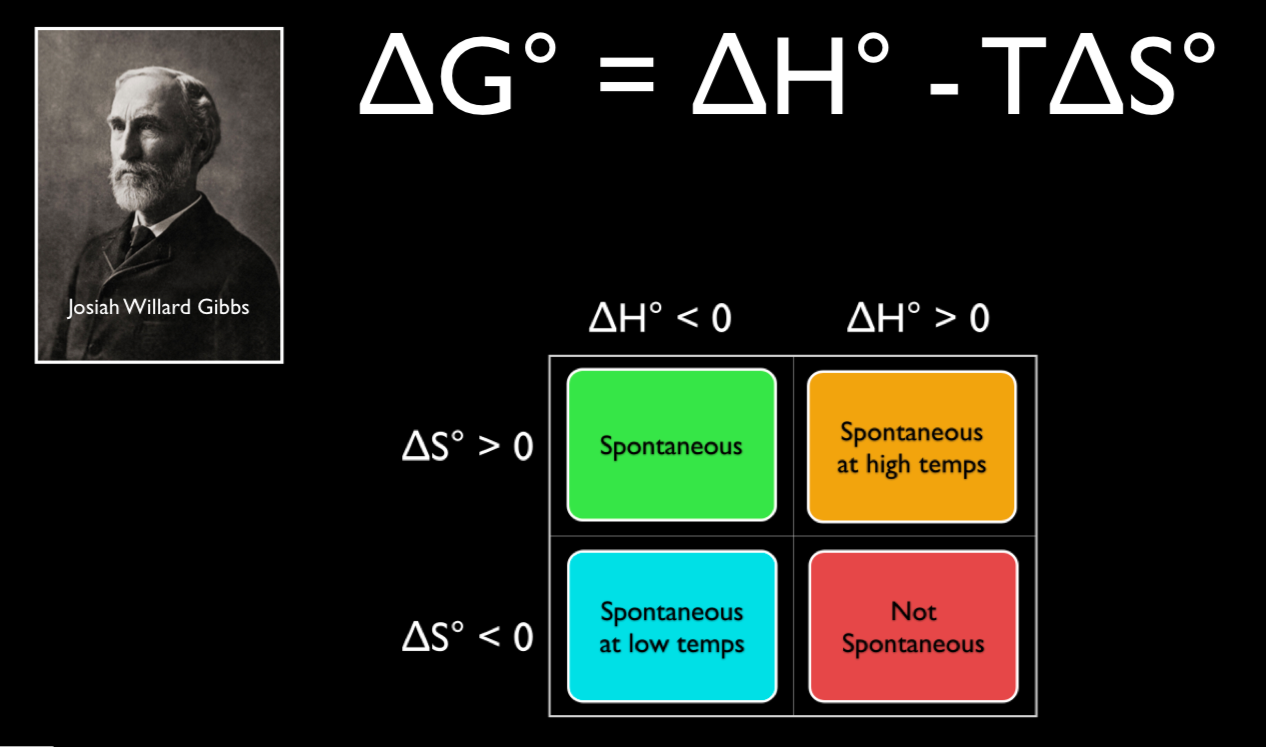
1800s, Josiah Willard Gibbs, (19-1903) submitted scientific papers which mathematically combined both enthalpy and entropy (the measure of energy release and disorder in a system respectively) that also incorporates the second law of thermodynamics:. Calculating an Equilibrium Constant from the Free Energy Change. We can use the relationship between ΔG ° and the equilibrium constant K, to obtain a relationship between E ° cell and K.
Rearrange the Gibbs free energy equation (G = H-T S) to solve for the temperature at a phase transition. Then Delta S = 16.77 J per Kelvin- mole. It is a thermodynamic property that was defined in 1876 by Josiah Willard Gibbs to predict whether a process will occur spontaneously at constant temperature and pressure.
The change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG) for a system depends upon the change in enthalpy (ΔH) and the change in entropy (ΔS) according to the following equation:. The change in Gibbs free energy under nonstandard conditions, ΔG, can be determined from the standard change in Gibbs free energy, ΔG⁰:. By putting the values in equation ΔG = ΔH – TΔS:.
N 2 + 3H 2 🡪 2NH 3. Start studying Entropy and Free Gibbs Energy. A quantitative measure of the favorability of a given reaction at constant temperature and pressure is the change ΔG (sometimes written "delta G.
059 - Using Gibbs Free Energy In this video Paul Andersen explains how you can use the Gibbs Free Energy equation to determine if a process is spontaneous or. ΔG = ΔH - TΔS. The free energy of a system is the sum of its enthalpy (H) plus the product of the temperature (Kelvin) and the entropy (S) of the system:.
It gives 298 Delta S = 5000 J. 2NO_2 to N_2 O_4 Where Delta. The purpose of this calculator is to calculate the value of the enthalphy of a reaction (delta H) or the Gibbs free energy of a reaction (delta G).
Δ r G, Gibbs free energy change per mole of reaction, Δ r G°, Gibbs free energy change per mole of reaction for unmixed reactants and products at standard conditions (i.e. Δ G = Δ G ⁰ + RT ln Q where R is the ideal gas constant 8.314 J/mol K, Q is the reaction quotient, and T is the temperature in Kelvin. It is named after Josiah Willard Gibbs and Hermann von Helmholtz.
Gibbs Free Energy (G) - The energy associated with a chemical reaction that can be used to do work. D G = D H - T D S. T = - G d.
If delta G is positive, the. Free energy (Gibbs) the combined. C 3 H 8 (g)-24.
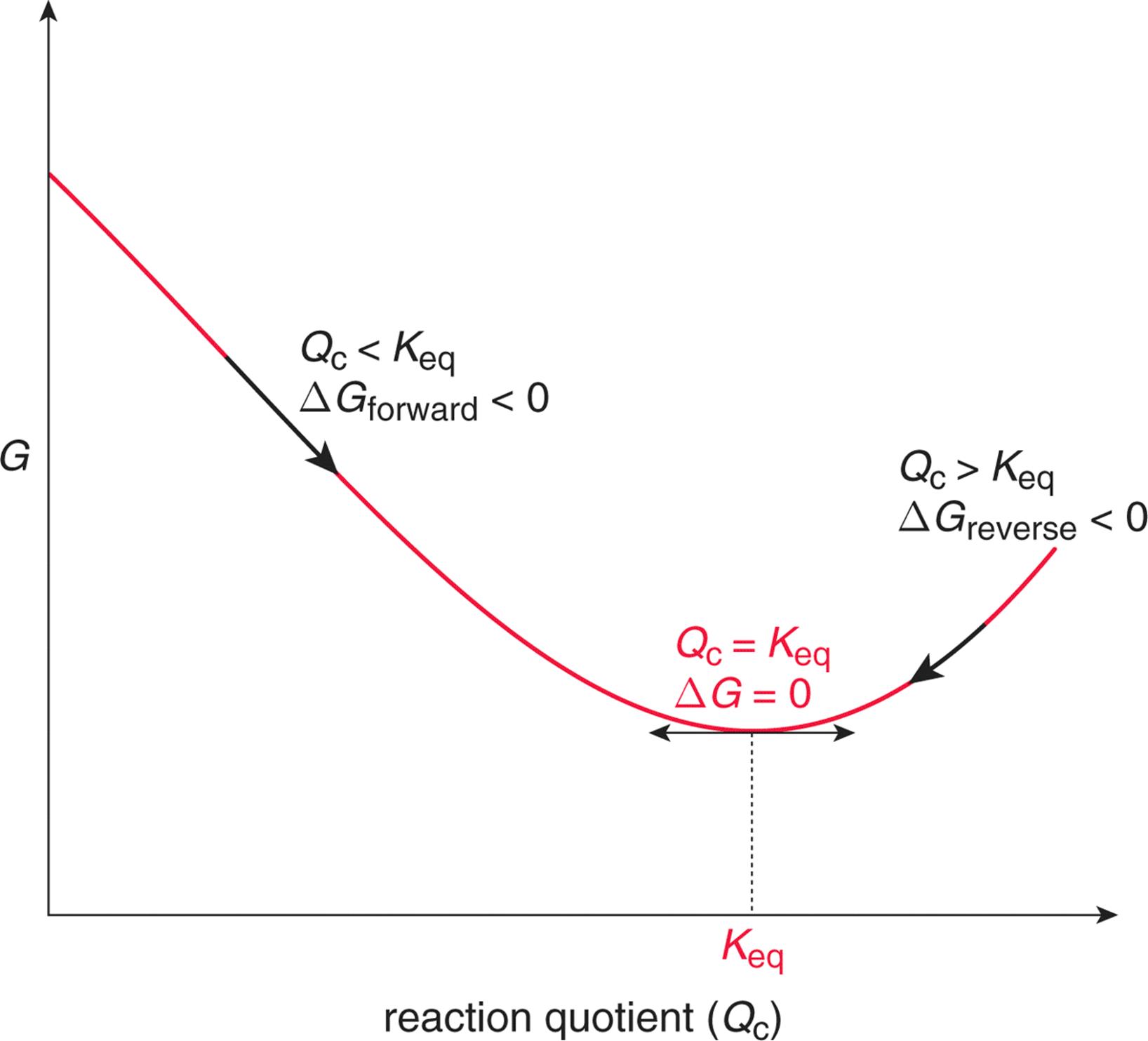
Gibbs free energy is a measure of the potential for reversible or maximum work that may be done by a system at constant temperature and pressure. The derivation that was written in the post was as follows:. So this is our reaction quotient.
Gibb's free energy equation. The change in Gibbs energy is. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
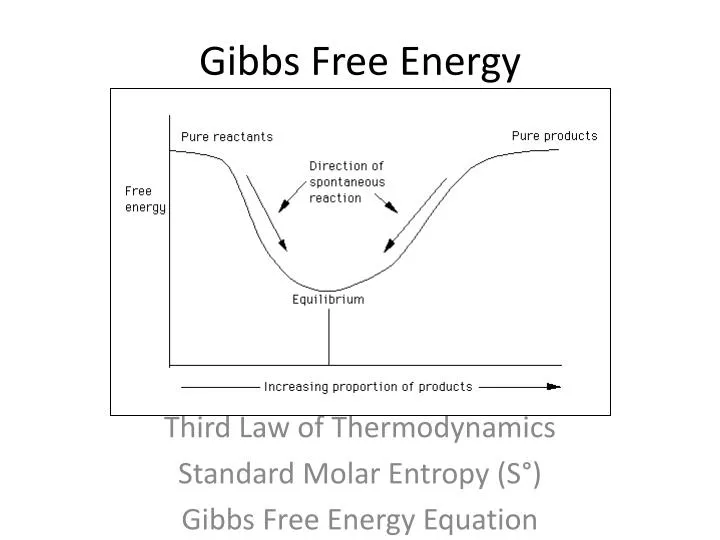
The Gibbs Free Energy of a reaction, delta G, can be calculated through the equation delta G = delta H - T*delta S. Delta G = Delta H - T Delta S. The ΔG (Gibbs free energy change) of a system at equilibrium is 0.
Δ G = Δ G ⁰ + RT ln Q where R is the ideal gas constant 8.314 J/mol K, Q is the reaction quotient, and T is the temperature in Kelvin. ΔG° It is important to realise that we are talking about standard free energy change here - NOT the free energy change at whatever temperature the reaction was carried out. Gibbs free energy G is defined as.
R is the gas constant with a value of 8.314 J K-1 mol-1. ΔG° = ΔH° - TΔS° That's all you need to know. Continuing with the topic of Equilibrium, I'm getting into the equilibrium constant and clarifying the definitions of enthalpy (delta H) and entropy (delta S) and applying that information to the spontaneity of reactions, summarized in Gibbs free energy (delta G).
G = H - T D S. Free energy of reaction (G). Gibbs Free Energy Equation This is.
Changes in free energy and the reaction quotient. In order to measure the amount of free energy present within any given. Delta G= Delta H- (T * Delta S) Negative Delta G.
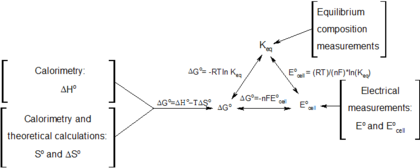
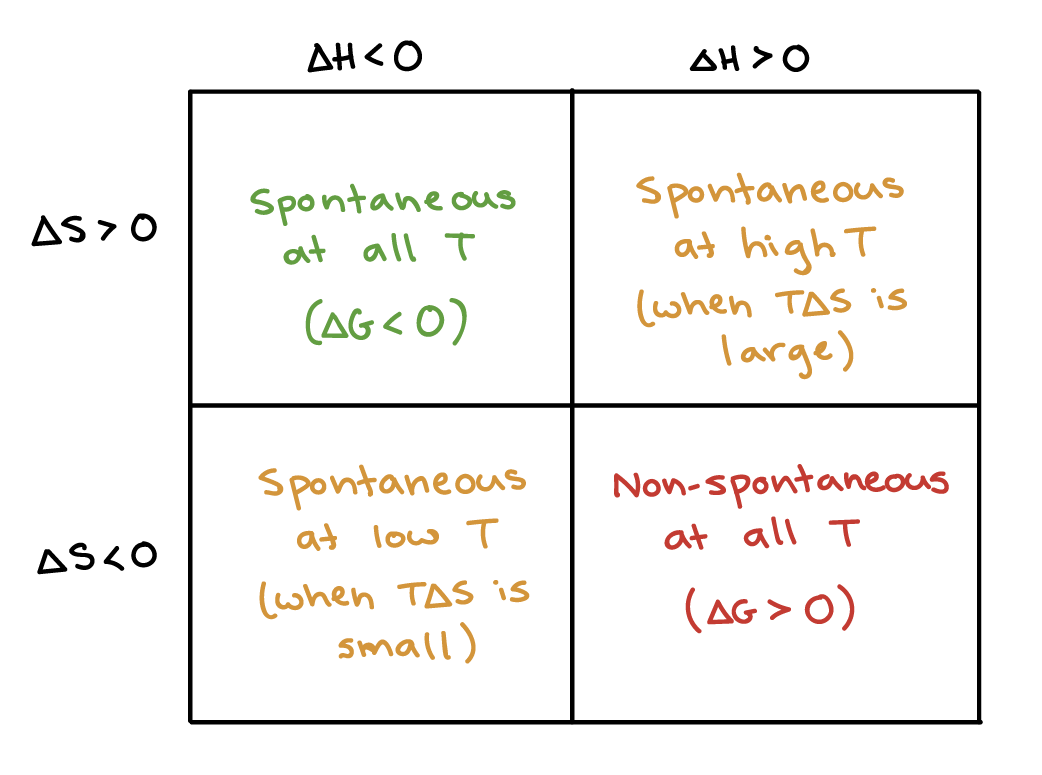
Depending on the sign and magnitude of each, the sum of these terms determines the sign of Δ G and therefore the spontaneity (Table 18.2 “Spontaneity and the Signs of Enthalpy and Entropy Terms”). CH 2 =CHCN(g) 195. Calculate the change in standard free energy for the given reaction at a temperature of 25 degree Celsius.
This serves as a measurement of whether or not a reaction will spontaneously occur. G = H - T S. The Gibbs energy or Gibbs free energy (G) is a state function that depends on the state functions enthalpy (H) and entropy.
Gibbs Free Energies of Phases All phases, whether mineralogical or not, have an associated Gibbs Free Energy of Formation value abbreviated Δ G f.The Δ G f value describes the amount of energy that is released or consumed when a phase is created from other phases. C 2 H 2 (g) 210. It is a convenient criterion of spontaneity for processes with constant pressure and temperature.
T = H/ S c. The Gibbs' free energy of mixing for an ideal binary solution is calculated using this equation:. The change in Gibbs free energy under nonstandard conditions, ΔG, can be determined from the standard change in Gibbs free energy, ΔG⁰:.
\E^o = E^o_{reduction} - E^o_{oxidation} \label{1}\ \(\Delta{G}\) is also related to \(E\) under general conditions (standard or not) via \\Delta{G} = -nFE \label{2}\ with \(n\) is the number of electrons transferred in the reaction (from balanced reaction),. ΔG = ΔH - TΔS. The problem is to pump glucose into the cell (where it is about 0.5 mM ) and then across the plasma membrane at the basolateral surface of the cell into the interstitial fluid , where the glucose concentration is 5 mM (the same as in the.
The Equation edit Free energy is defined by Δ G = Δ H − T Δ S {\displaystyle \Delta G=\Delta H-T\Delta S}. If we know the standard state free energy change, G o, for a chemical process at some temperature T, we can calculate the equilibrium constant for the process at that temperature using the relationship between G o and K. Entropy can never decrease, only increase for a reaction to take place.
Delta G = Delta H - (T)(Delta S). Standard change in free energy and the equilibrium constant. In the previous equation:.
Free energy is a combination of entropy and enthalpy, and when a reaction decreases the free energy, it will occur spontaneously. ΔGo = ΔHo - TΔSo. T is the temperature of the reaction in Kelvin.
C 2 H 5 OH(l)-175. Rearrangement gives In this equation:. Gibbs energy or Gibbs function;.
State whether or not the reaction will be spontaneous. Enthalpy and Gibbs Free Energy Calculator Introduction :. The equation states that the change in the G/T ratio at constant.
The free energy change, D G is equal to -T D S univ and it applies just to a system itself, without regard for the surroundings. Both endergonic and exergonic reactions require a small amount of energy to overcome an activation barrier. The Relationship between ΔG, ΔH, and ΔS.
Consider, for example, enstatite (MgSiO 3).The Gibbs Free Energy of Formation for enstatite from pure elements (Mg, Si and O. \mathbf(Delta_"mix"G^"id" = RTn_ilnchi_i + n_jlnchi_j) It gets more complicated with nonideal solutions though, as you have to incorporate the activity coefficient gamma_j = a_j/chi_j = (P_j)/(chi_jP_j^"*") (from Raoult's law). It is defined by the Gibbs equation:.
The Gibbs Free Energy (delta G) is equal to the enthalpy (delta H) minus the temperature in Kelvin times the entropy (delta S). Gibbs energy (also referred to as ∆G) is also the chemical potential that is minimized when a system reaches equilibrium at constant pressure and temperature. Calculate Delta G using the.
Delta G of a system is the difference between change in enthaly and the product of K temp and entropy change. Gibbs Free energy formula is given below. Willard Gibbs defined a function known as Gibbs energy (G), to calculate the changes in entropy and enthalpy values.
Surface tension, Gibbs free energy and critical micelle concentration?. According to the second law of thermodynamics, for systems reacting at standard conditions for temperature and pressure (or any other fixed temperature and pressure), there is a general natural tendency to achieve a minimum of the Gibbs free energy. In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy (IUPAC recommended name:.
@yuri how about equation with delta G= (2-beta) RTln cmc and also another equation with delta G=(1+beta). The Gibbs free energy equation is dependent on pressure. C 2 H 4 (g) 68.
Standard Gibbs free energy change, ΔG° Calculating ΔG° This is how standard Gibbs free energy change is calculated:. A look at a seductive but wrong Gibbs spontaneity proof. Delta G - Free energy change (KJmol-1) Delta H - Enthalpy change (KJmol-1) Temperature - K (usually 293) Delta S - Entropy (KJ mol) always divide by.
Solved Numerical on Gibbs Free Energy. Gibbs Free Energy Zn(s) + Cu2+ (aq) --> Zn2+ (aq) + Cu(s) At 25 C, the cell potential was 0.874V. I want to understand the derivation between gibbs energy and equillibrium constant $$\Delta G=\Delta G^o+RT\ln Q?$$ I have seen a similar post on CSE Derivation of relationship between equilibrium constant and Gibbs free energy change which seems to be incomplete and still confusing so I am again asking this question.
Free Energy and Free Energy Change —the Gibbs free energy, G, is used to describe the spontaneity of a process. The temperature dependence at a phase transition can be determined from thermodynamics. The form below provides you with blanks to enter the individual enthalpies or free energy d ata points for a given reaction.
159.1 x 1000 J = 164.1 x 1000 J - 298 xDelta S. Delta H and S are -81.5 KJ and -1.0 J/K, respectively. The change in Gibbs free energy for any chemical process is actually written as Delta G.
ΔG° = − RTlnK. Calculate Delta G using Gibbs Free Energy equation. P = − H T 2, {\displaystyle \left_{p}=-{\frac {H}{T^{2}}},} where H is the enthalpy, T the absolute temperature and G the Gibbs free energy of the system, all at constant pressure p.
What is the free energy needed to move glucose back from the tubular fluid to the blood when the concentration in the tubular fluid has dropped to 0.005 mM?. We're gonna plug this into our equation and we're gonna solve for delta G. Standard free energy change is easily calculable from the equilibrium constant.Standard free energy change must not be confused with the Gibbs free energy change.
ΔG° = -RT ln K. C 2 H 4 O(g) (ethylene oxide)-13. The change in the Gibbs free energy of the system that occurs during a reaction is therefore equal to the change in the enthalpy of the system minus the change in the product of the temperature times the entropy of the system.
G = H - (TS) If the reaction is run at constant temperature, this equation can be written as follows. So delta G is equal to delta G zero, the standard change in free energy. G = H - TS.
C 3 H 6 (g) 63. There are a three tricky points to remember about Gibbs free energy. Explain the nature of the equilibrium constant, define various variations of the equilibrium constant, and write an.
The Gibbs–Helmholtz equation is a thermodynamic equation used for calculating changes in the Gibbs energy of a system as a function of temperature. The Nernst Equation is derived from the Gibbs free energy under standard conditions. This chemistry video tutorial discusses the relationship between cell potential and gibbs free energy.
Given that the temperature (T) and pressure (P) of the system are constant, you can write the equation for Gibbs free energy as follows:. If delta G is negative, a reaction is said to be spontaneous;. The maximum work done is the amount of energy produced, given by the decrease in the thermodynamic property called Gibbs free energy.
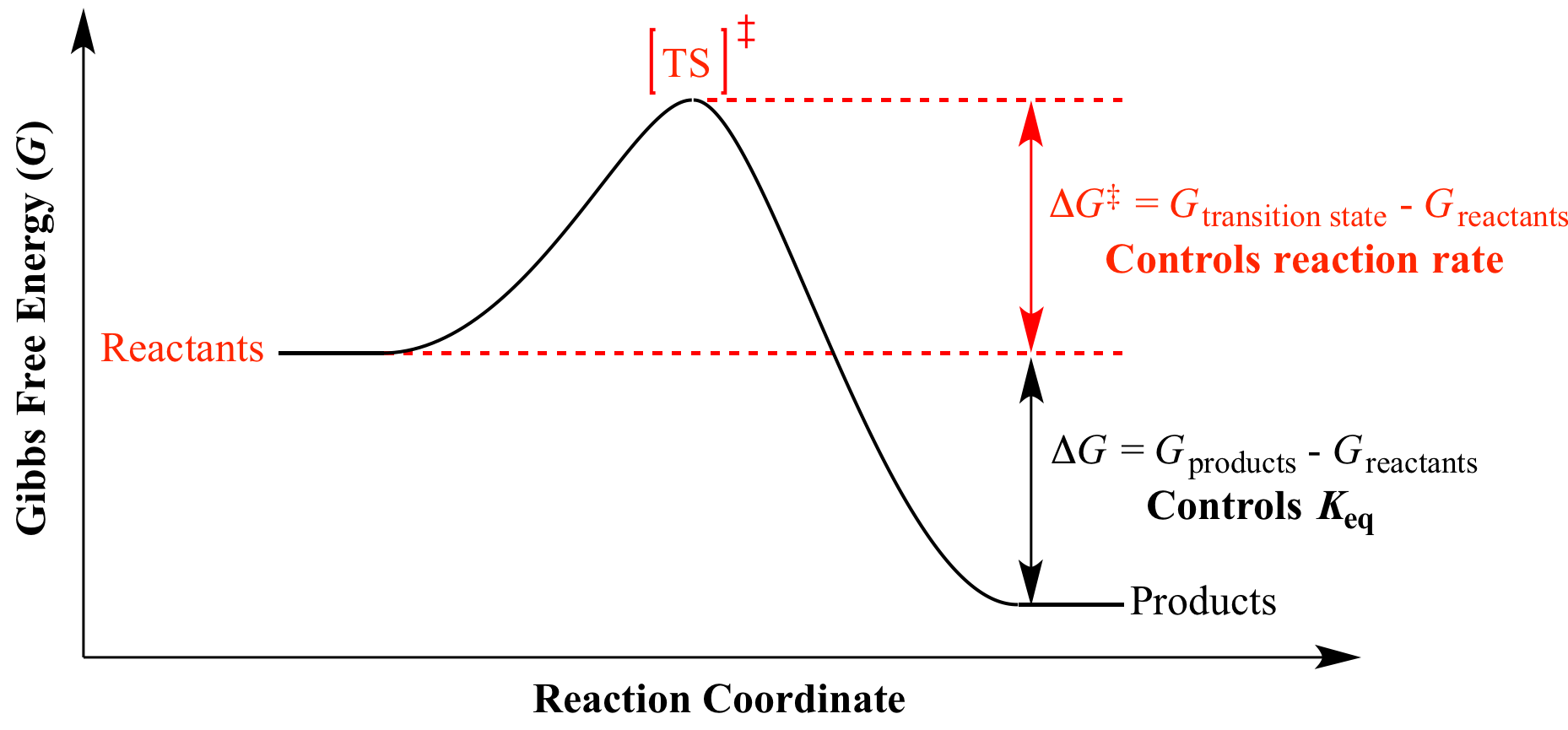
More rigorous Gibbs free energy / spontaneity relationship. We need to make that joules so I'm gonna say times 10 to the third joules. The delta G of a reaction is the free energy of the final state minus the free energy of the initial state, making it is independent of the reaction pathway.
Delta H is the change in enthalpy, T is the temperature in degrees Kelvin and delta S is the change in entropy.
Chapter 9 Lecture Notes
Gibbs Free Energy

17 1 Equilibrium And Gibbs Free Energy Hl Youtube
Delta G Gibbs Free Energy Equation のギャラリー

Pin On 13 Thermodynamics
Gibbs Free Energy Thermochemistry Training Mcat General Chemistry Review
Ppt Gibbs Free Energy Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Chemical Thermodynamics Gibbs Free Energy Analytical Chemistry Video Clutch Prep

Ch 19 Spontaneity Thermodynamically Favored Entropy And Free Energy Ppt Download
Gibbs Free Energy Equilibrium Constant Mastering Chemistry

Thermodynamics What Is An Intuitive Explanation Of Gibbs Free Energy Quora

Gibbs Free Energy Equilibrium Constant Enthalpy Entropy Equations Free Energy Projects Free Energy Free Energy Generator

Reaction Quotient And Gibbs Free Energy At The Start Of A Reaction Chemistry Stack Exchange

Gibbs Free Energy And Spontaneity Video Khan Academy

Topic 15 Energetics Hl Msjchem Tutorial Videos For Ib Chemistry
Chem 245 Equilibrium And Free Energy

Activation Energy
Free Energy Delta G Calculations Pt 7 Youtube

The Relationship Between Free Energy And The Equilibrium Constant Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Solved Calculate The Standard Change In Gibbs Free Energy Chegg Com
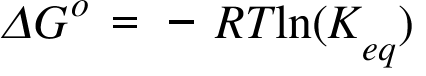
Standard Free Energy Change And Equilibrium Constant Calculator Calistry

Gibbs Free Energy
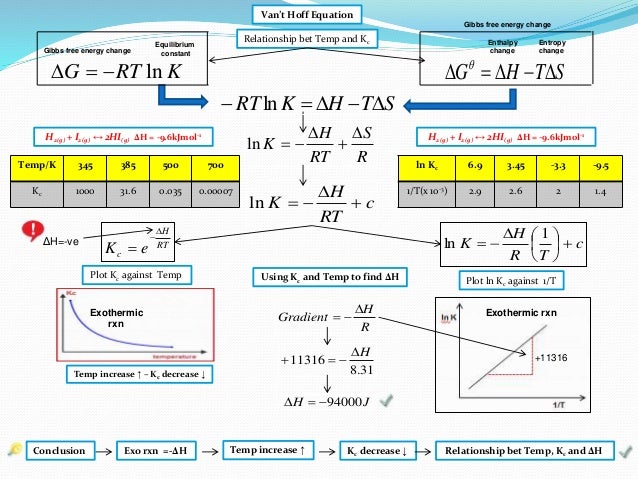
Ib Chemistry On Gibbs Free Energy And Equilibrium Constant Kc

Gibbs Free Energy

Cell Potential Gibbs Free Energy Standard Reduction Potentials Electrochemistry Problems Youtube
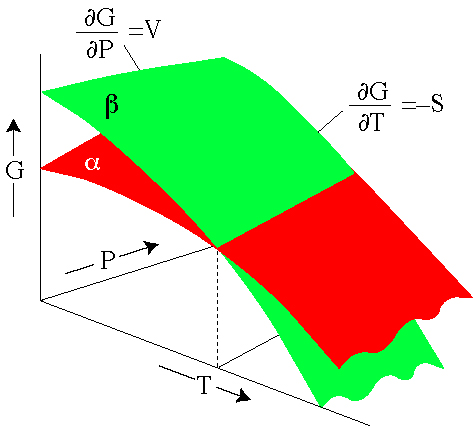
Gibbs Energy
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqydv7umvmzpsssheiiluymavmruyefuqldgudklenw5mdln8tk Usqp Cau

Wikipremed
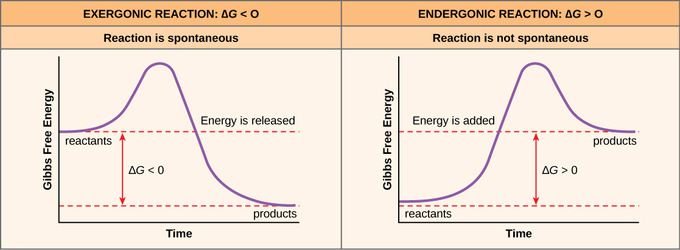
Free Energy The School Of Biomedical Sciences Wiki

Gibbs Free Energy Changes Equation Calculations Reaction Feasibility Extraction Of Metals Cell Emf Gce A Level Chemistry Revision Notes
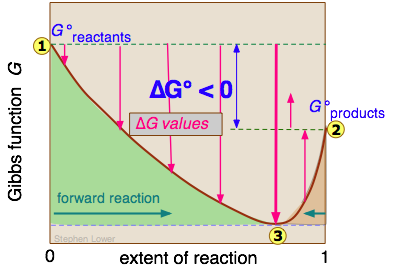
Free Energy And Equilibria
Data Analysis For Boiling Water Gibbs Free Energy Chegg Com

Gibbs Free Energy Equilibrium Constant Enthalpy Entropy Equations Practice Problems Youtube
How Is Gibbs Free Energy Related To Enthalpy And Entropy Socratic

Gibb S Free Energy And The Nature Of Chemical Reactions

Gibbs Free Energy And Equilibrium By Mr Campisi S Chemistry Apothecary
Gibbs Free Energy Wikipedia
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs4pqwasztj8vdgiebgeyehl8z8oofviuzhglutttyjwtb6dlby Usqp Cau

Calculations Of Free Energy And Keq Ck 12 Foundation
Gibbs Free Energy And Spontaneity Article Khan Academy
Connection Between E Cell G And K Chemistry Libretexts

Department Of Chemistry And Biochemistry Chem 45 Metabolic Processes

Temperature In The Gibbs Free Energy Equation Chemistry Stack Exchange
Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Dg

Spontaneity Free Energy And Temperature Introductory Chemistry
Chemical Potential And Gibbs Free Energy
How To Interpret Thermodynamics Of Reactions Organic Chemistry Help

What Is Meaning Of All The Symbpls In Gibbs Free Energy Equation Google Search Free Energy Free Energy Projects Energy

Gibbs Free Energy Lab Plan Ch 233 General Chemistry 233 Studocu

Gibbs Free Energy Temperature And Spontaneity Ppt Download

Gibbs Free Energy Antisense Science
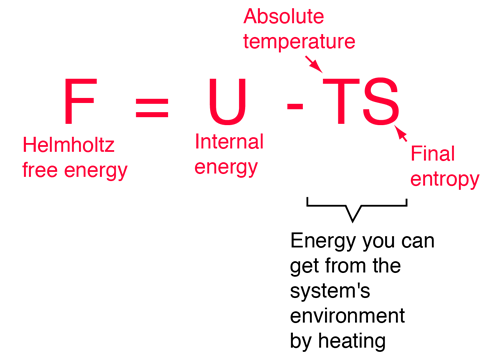
Helmholtz And Gibbs Free Energies

6 2 Potential Kinetic Free And Activation Energy Texas Gateway

Gibbs Free Energy Free Energy Teaching Chemistry Physical Chemistry

Department Of Chemistry And Biochemistry Chem 45 Metabolic Processes
Unit 10 11 Thermochemistry Thermodynamics Mrs Forest S Chemistry Class Website

The Relationship Between Free Energy And The Equilibrium Constant Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Gibbs Free Energy G

Gibbs Free Energy
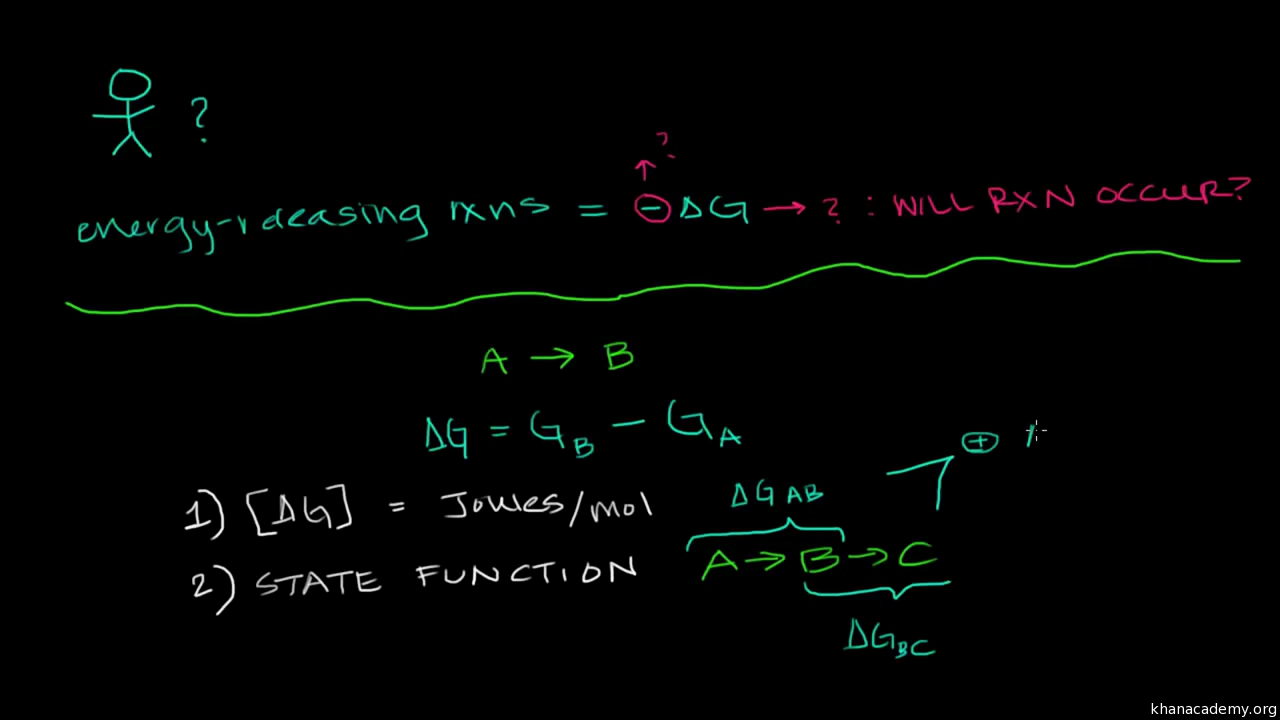
Gibbs Free Energy Introduction Video Khan Academy
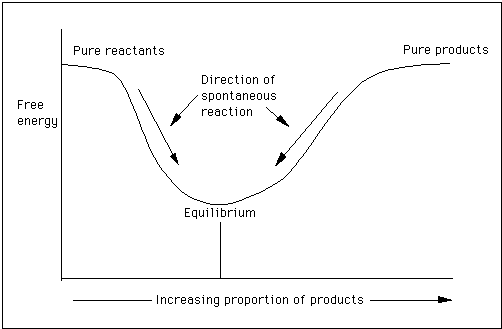
Chemical Thermodynamics

The Relationship Between Free Energy And The Equilibrium Constant Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

How Does The Principle Of Entropy Fit With What We Know Or Suspect About Abiogenesis Quora

17 1 Equilibrium And Gibbs Free Energy Hl Youtube
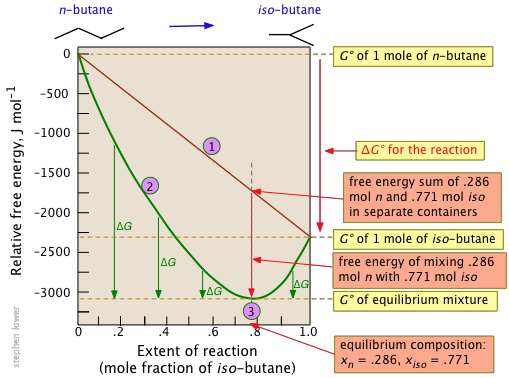
Free Energy And Equilibrium Chemistry Libretexts
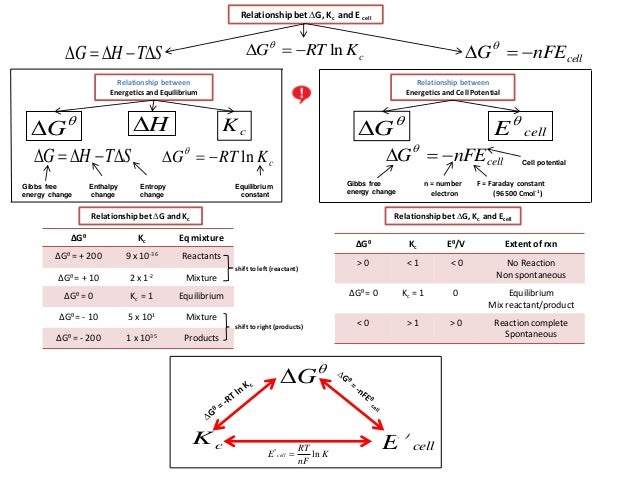
Ib Chemistry On Gibbs Free Energy Equilibrium Constant And Cell Pote

Gibbs Free Energy G
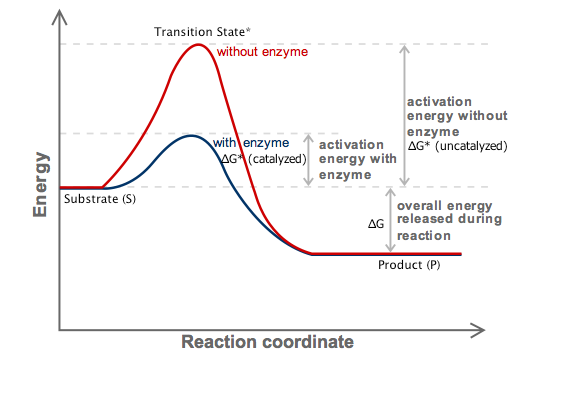
How Do Enzymes Affect Gibbs Free Energy Socratic

Calculations Of Free Energy And Keq Ck 12 Foundation
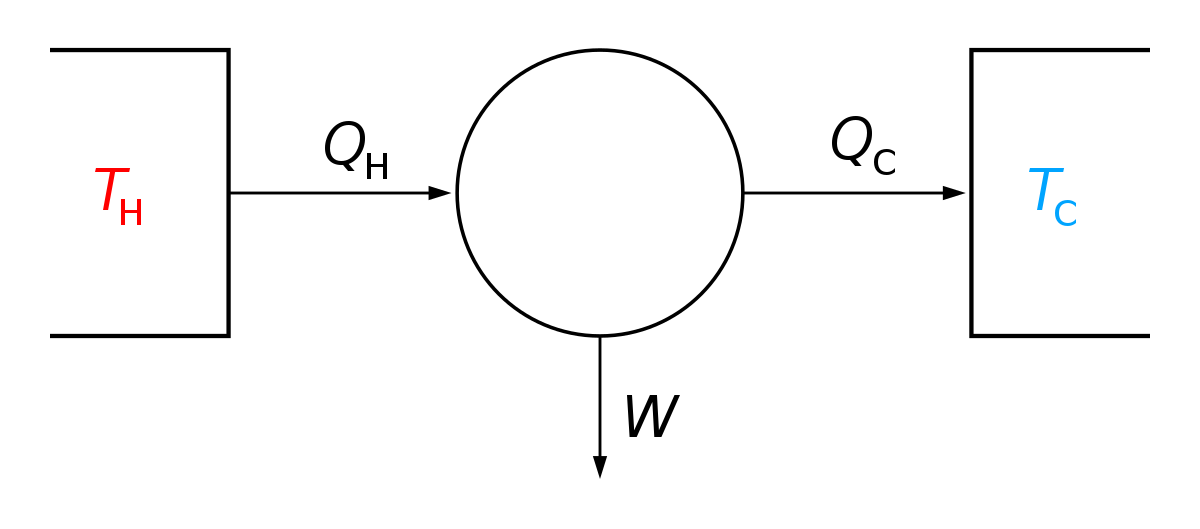
Gibbs Free Energy Wikipedia

Gibbs Free Energy Calculator

Understanding Gibbs Free Energy Surfguppy Chemistry Made Easy For Visual Learners

Gibbs Energy And Equilibrium Constants Youtube
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr8vjttktf0pl5rumwvlt Df0j3ikrkvlwb Ulepnz97okfyyrw Usqp Cau
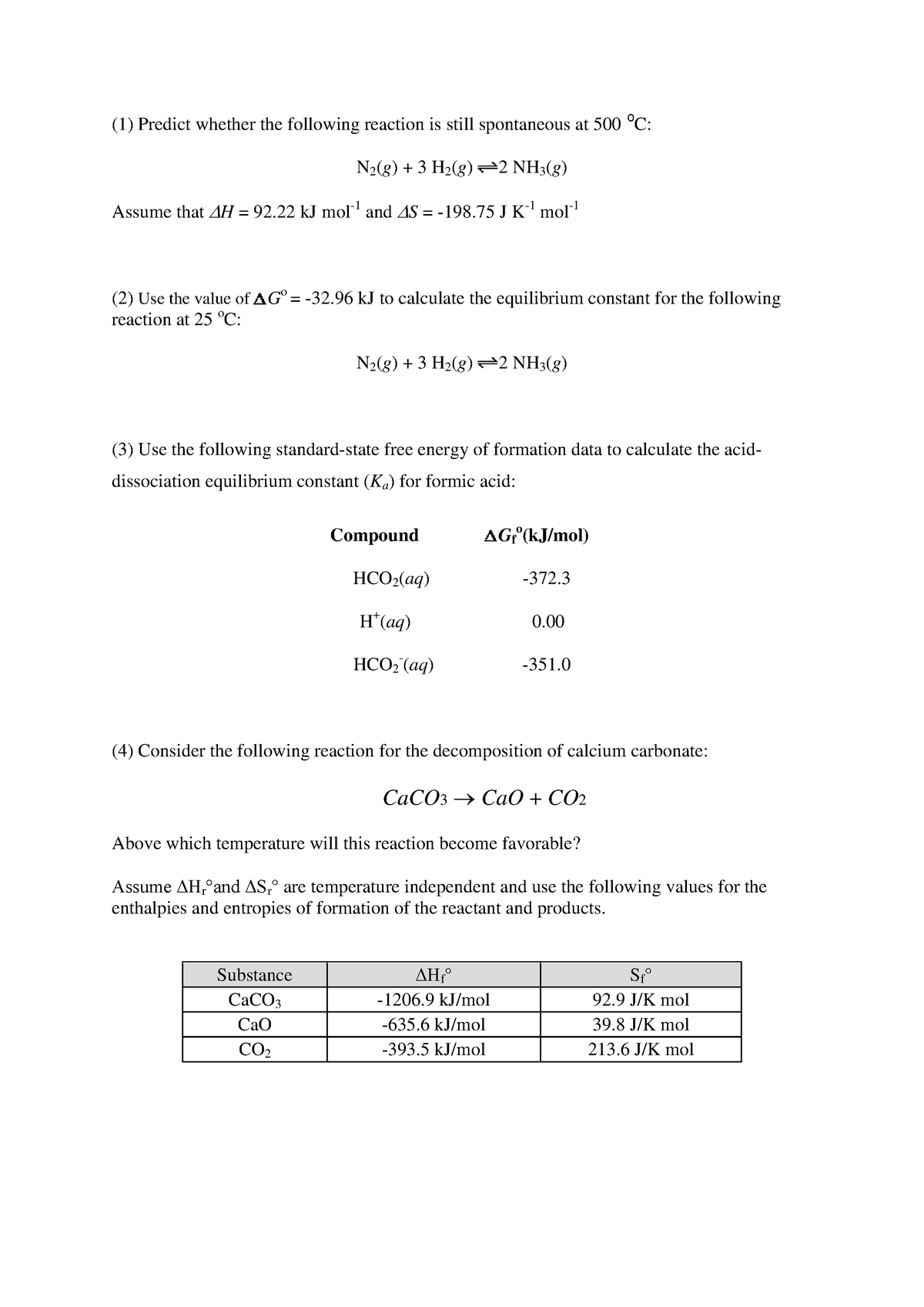
Gibbs Free Energy Worked Problems Studocu

Getting Gibbs Energy As A Function Of Temperature

Gibbs Free Energy Equilibrium Thermodynamics

Delta G Formula Calculator Academy

Gibb S Free Energy G Calculator
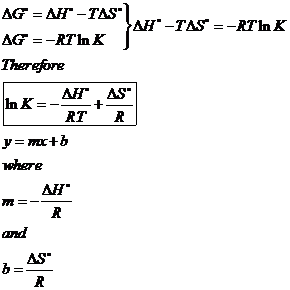
Gibbs Free Energy

Gibbs Free Energy Equilibrium Constant Enthalpy Entropy Equations Practice Problems Youtube

Calculate The Standard Change In Gibbs Fre Clutch Prep

Gibbs Energy And Reaction Diagrams Chemical Kinetics Flashcards Memorang
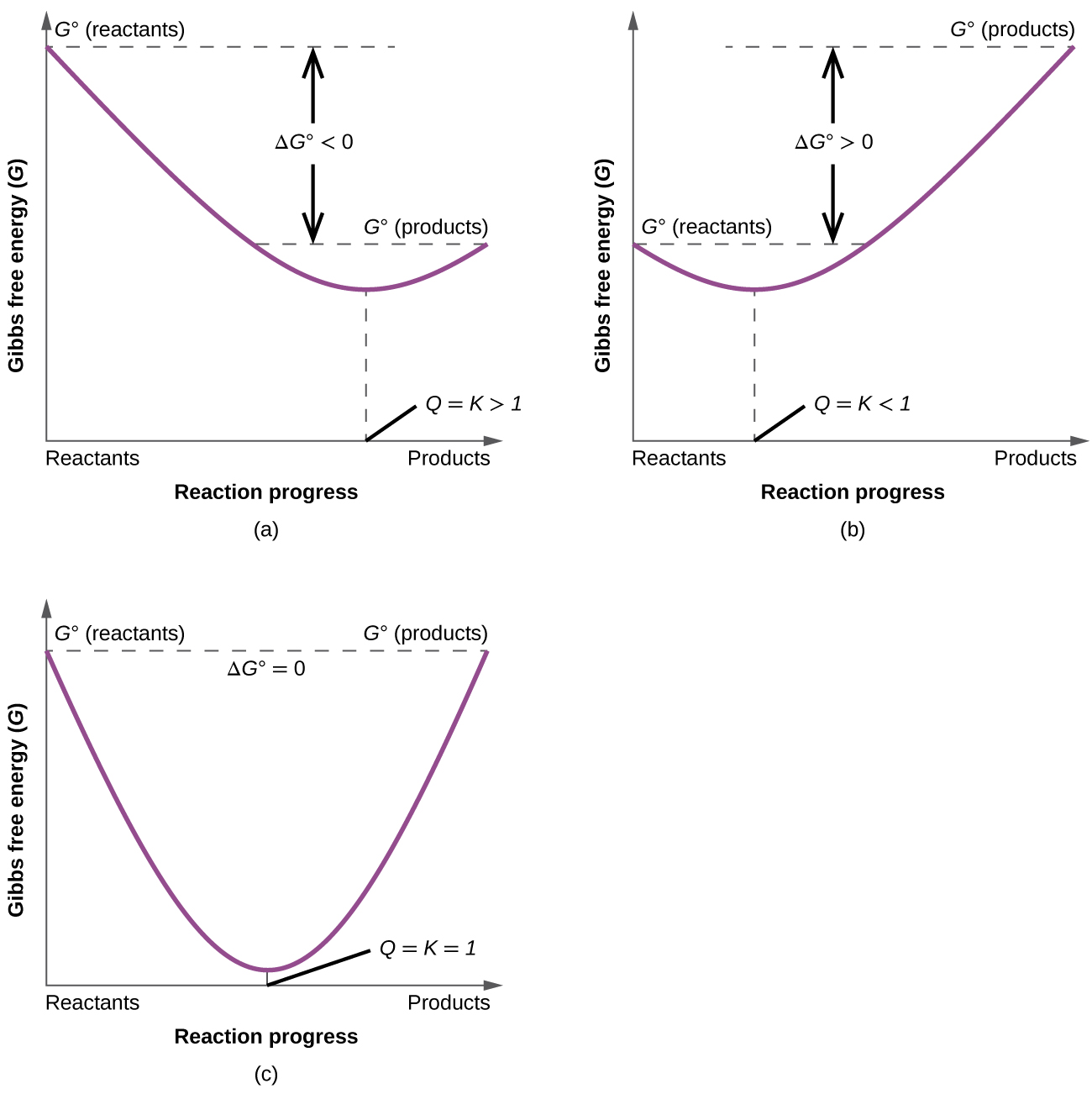
19 6 Gibbs Energy Change And Equilibrium Chemistry Libretexts

Oneclass Calculate The Standard Change In Gibbs Free Energy For The Following Reaction At 25 Degree

Solved For The Gibbs Free Energy Equation Delta G Delt Chegg Com

Structural Biochemistry Free Energy Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World

Chemistry Question Bank Mcat Flashcards Questions And Answers Quizlet

Membrane Transport

Is Gibbs Free Energy Related To The Rate Of A Reaction Quora

Gibb S Free Energy And The Nature Of Chemical Reactions

How Much Energy Is Released In Atp Hydrolysis
3

Free Energy Delta G And Equilibrium Pt 8 Youtube

Gibbs Free Energy Boundless Chemistry

Chemical Thermodynamics

Gibbs Free Energy

Equilibrium Reactions Formation Constants And Gibbs Free Energy Of Download Table

Gibbs Free Energy

Chapter 17 Lesson 2 Free Energy And Thermodynamics Ppt Download

Solved Calculate The Equilibrium Constant From The Standa Chegg Com

Solved Calculate The Change In Gibbs Free Energy At Stand Chegg Com

Equilibrium Chemical Materialpedia
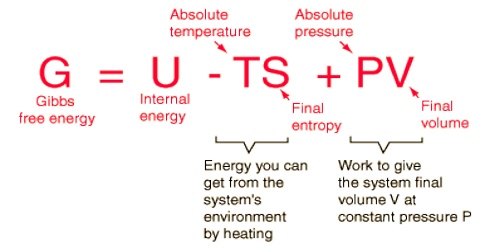
Helmholtz Free Energy And Its Significance Qs Study
Http Www Soest Hawaii Edu Oceanography Courses Ocn623 Spring13 Chemical Equilibrium 13 Handouts Pdf



