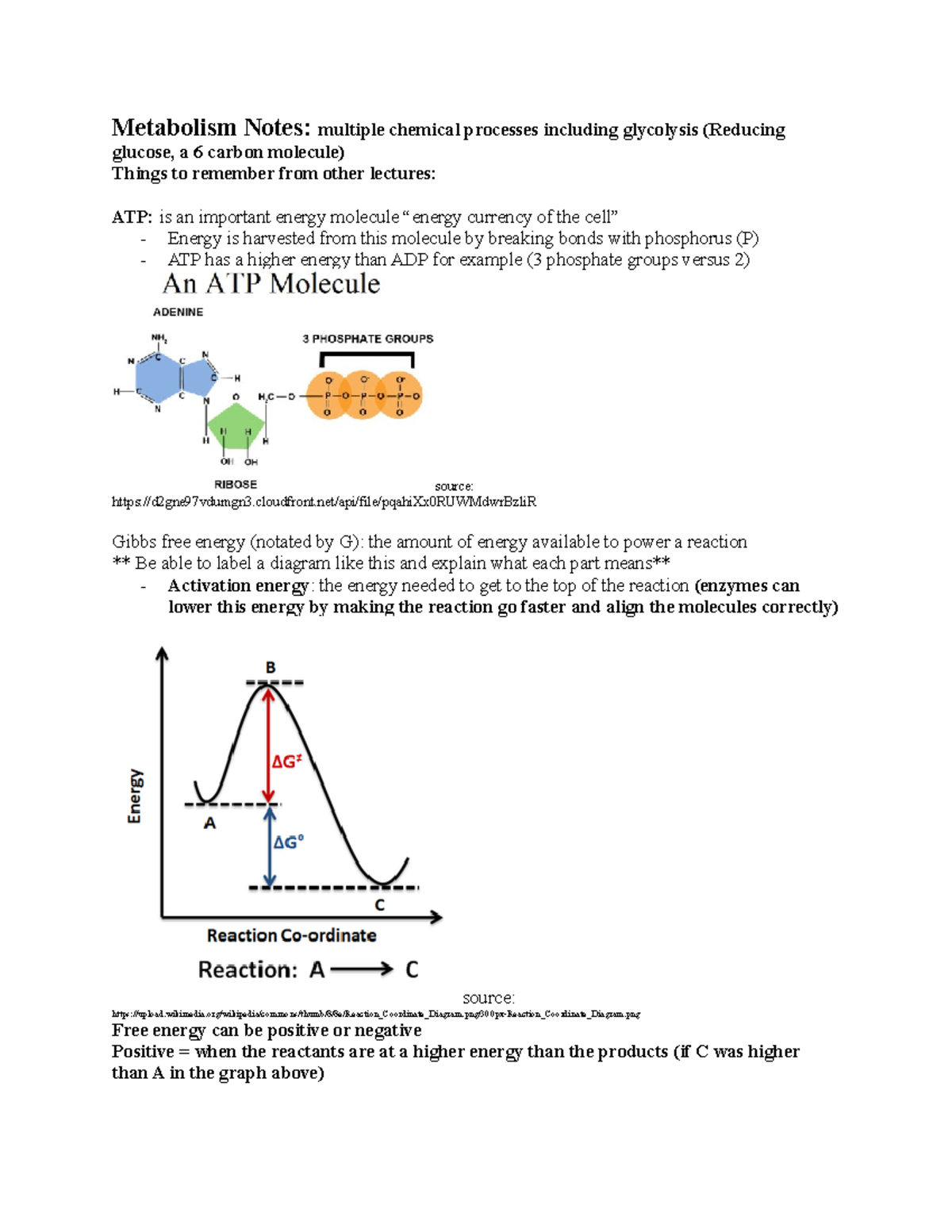
Gibbs Free Energy Graph Activation Energy
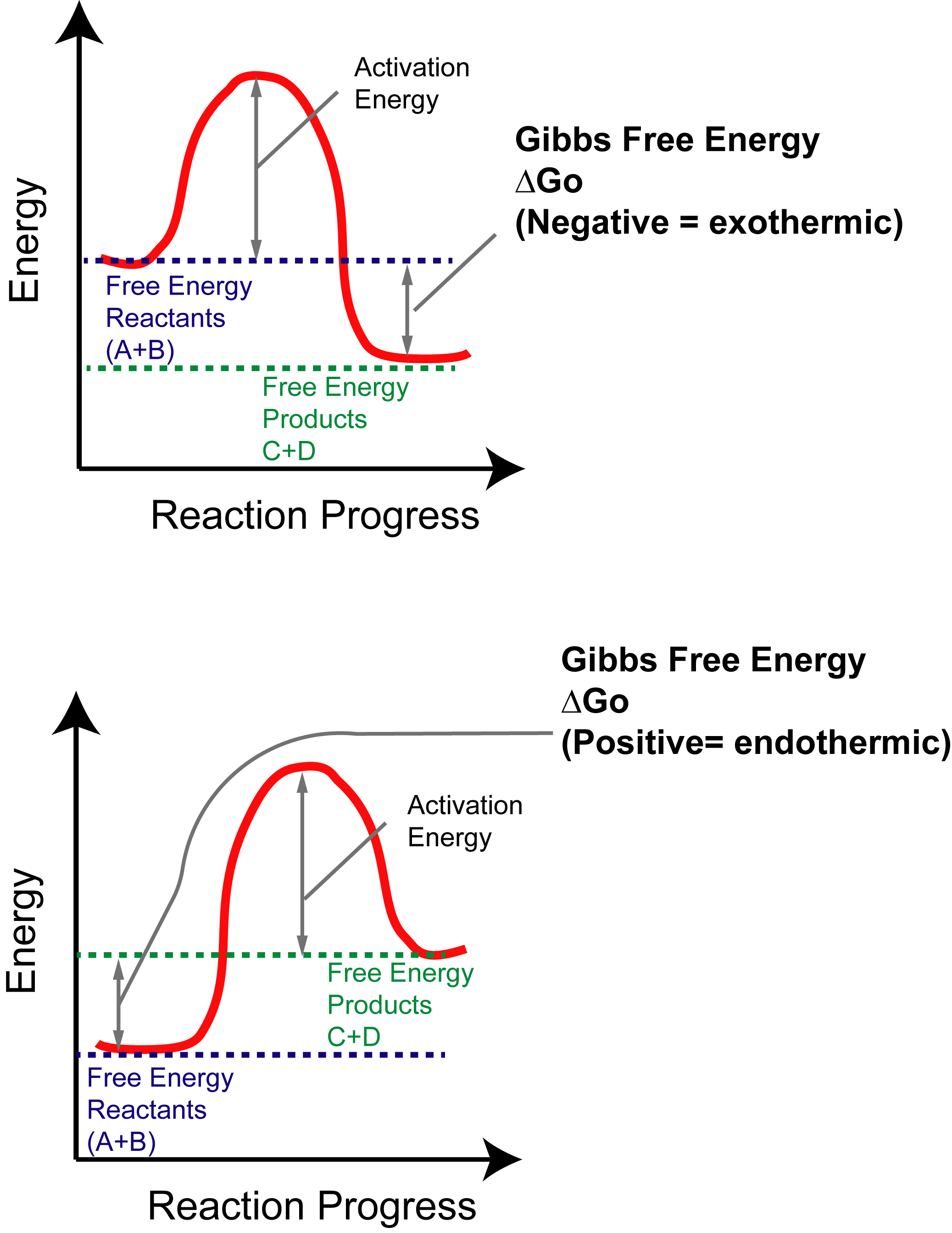
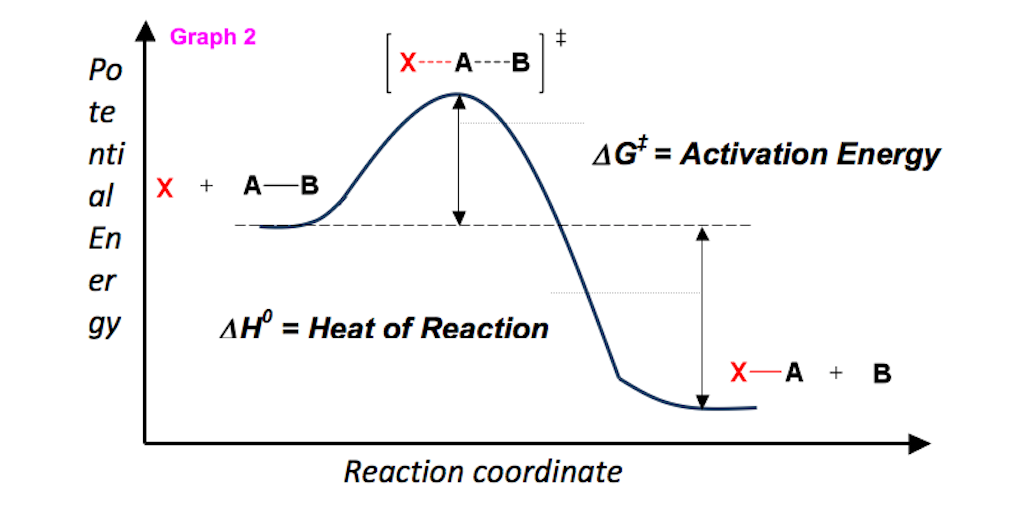
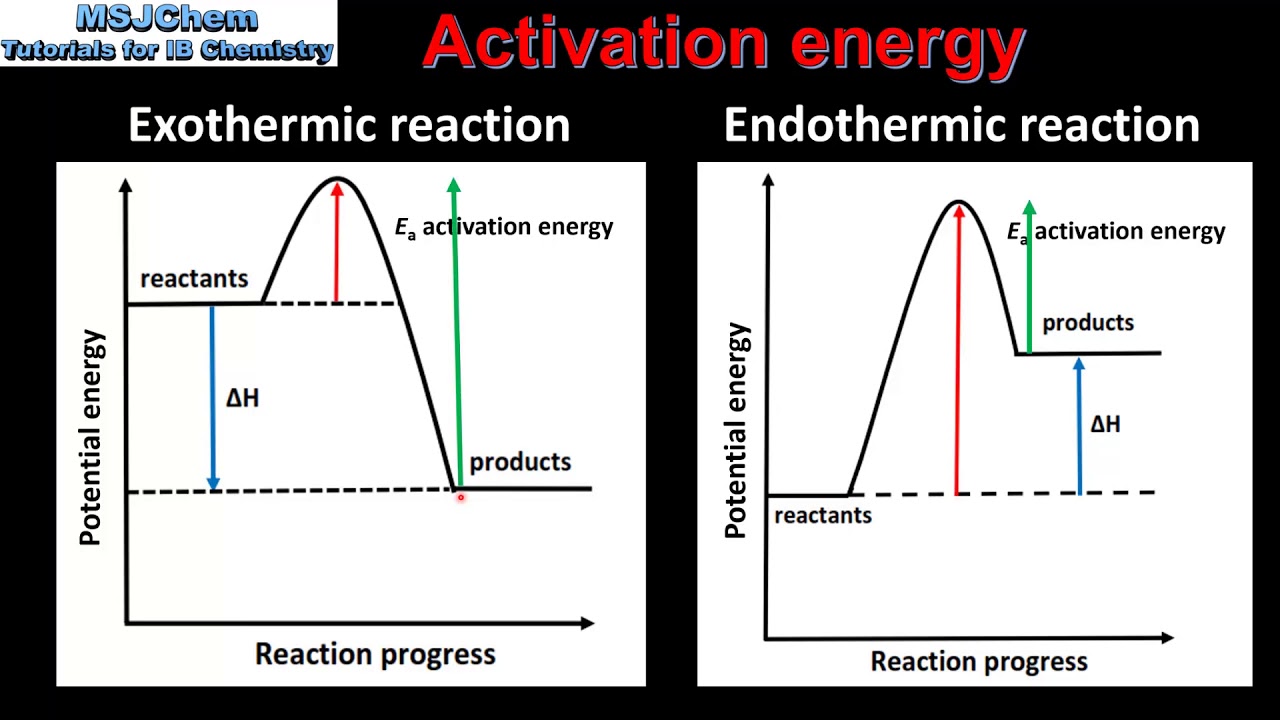
Because the reverse reaction's activation energy is the activation energy of the forward reaction plus ΔH of the reaction:.

Gibbs free energy graph activation energy. Another way to look at it is that the disorder or randomness of the system increases. All of the above e. Math\delta G /math describes the total amount of energy available to do work in a system whilst the activate energy mathE_{a} /math describes the highest energy state the system undergoes during said transition of state, therefore represen.
This is given by the relationship :. The Gibbs free energy of activation is:. Conversely if the Gibbs free energy of a process is positive it means that the process cannot take place (under the specified conditions).
PAC, 1994, 66. Gibbs Free Energy of Activation. Stability of these three forms by considering the Gibbs free energy.
In other words, Gibbs free energy is usable energy or energy that is available to do work. 1 Introduction Let Gbe a bipartite graph with color classes V and F. Gibbs Free Energy (G):.
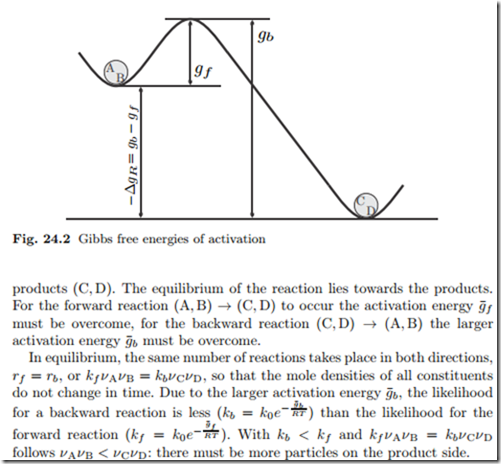
The rate of the reaction b. More specifically, we can write the Gibbs free energy of activation in terms of enthalpy and entropy of activation:. Graphs show how free energy changes with extent of reaction enables us to visualize a chemical reaction seeking its equilibrium position.
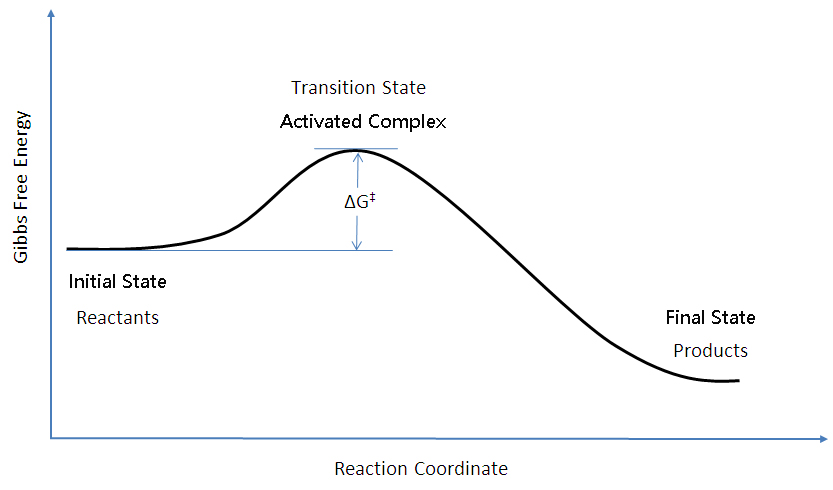
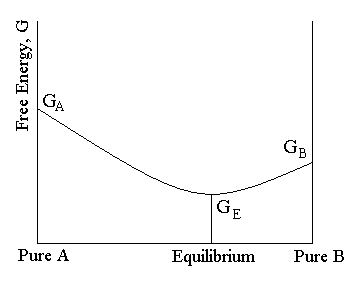
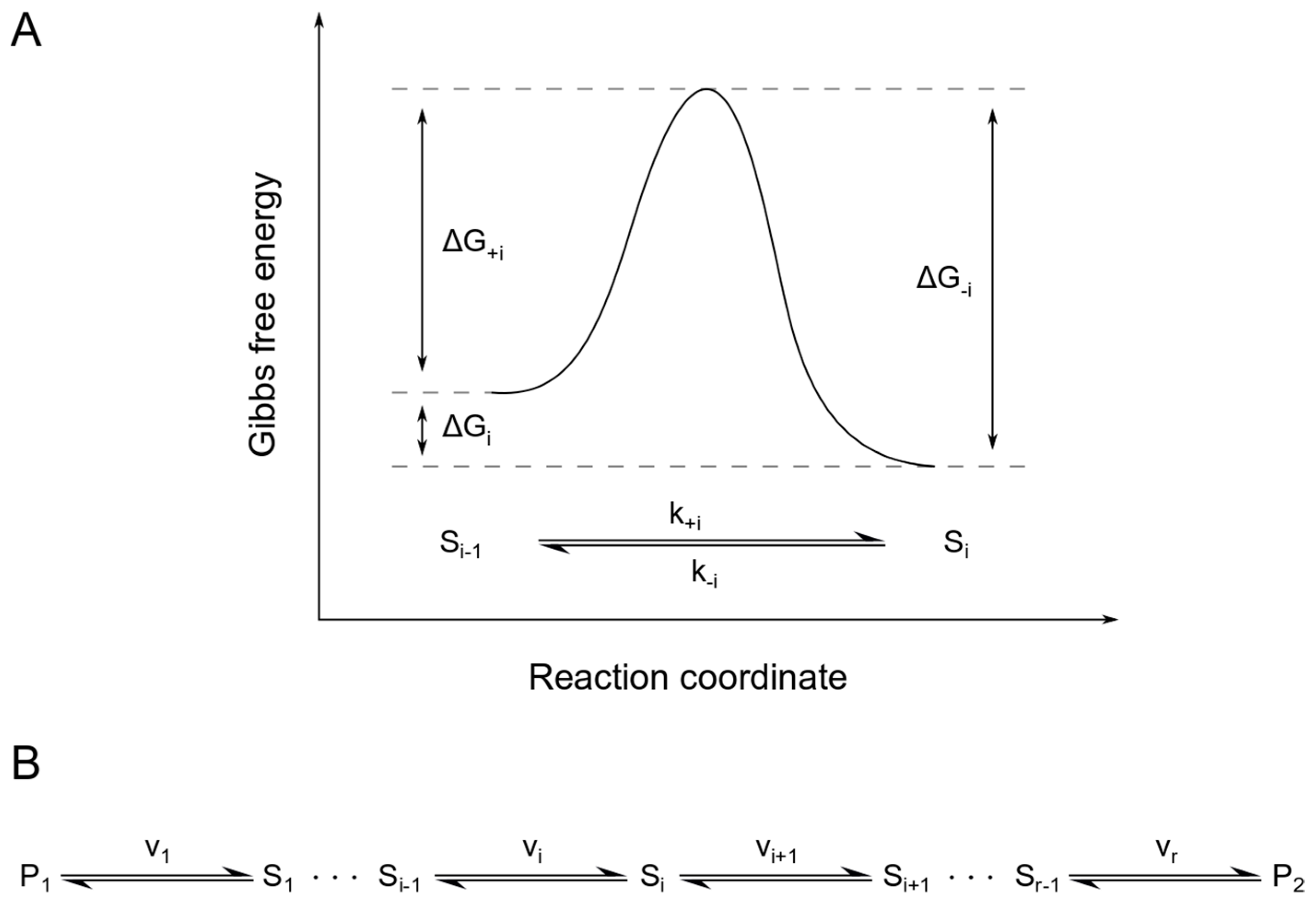
Thus, two equilibrium states which are characterized by local minima in free energy (G, stands for Gibbs free energy) are separated by a maximum represented by the activated state, as shown below:. Gibbs free energy and spontaneous reactions. Look at the graph of reaction rate versus substrate concentration for an enzyme.
Delta G is the change in Gibbs' Energy - energy released or energy required - to take a. A good illustration of this is found on page 76 of the course reader, which has a graph showing the reaction profile. In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy (IUPAC recommended name:.
MN is the section of the surface of dissipated energy. ΔG is the change in free energy. For a gas, the standard state is as a pure gaseous substance as a.
Therefore, as I mentioned before, we can go ahead and calculate. So if you had to calculate the Gibbs free energy change at, say, 298 K, you can just slot the numbers in:. The Eyring equation is another relation that describes the rate of reaction, except instead of using activation energy, it includes Gibbs energy of the transition state.
Gibbs Free Energy Change, ∆G Gibbs free energy is a term that combines the effect of enthalpy and entropy into one number The balance between entropy and enthalpy determines the feasibility of a reaction. CEM 142 Recitation Week 12 KEY Equilibrium & Gibbs Free Energy Graph 3 tells us what happens at the molecular level. Observe the reaction coordinate diagram for the formation of N2H4 and H2.
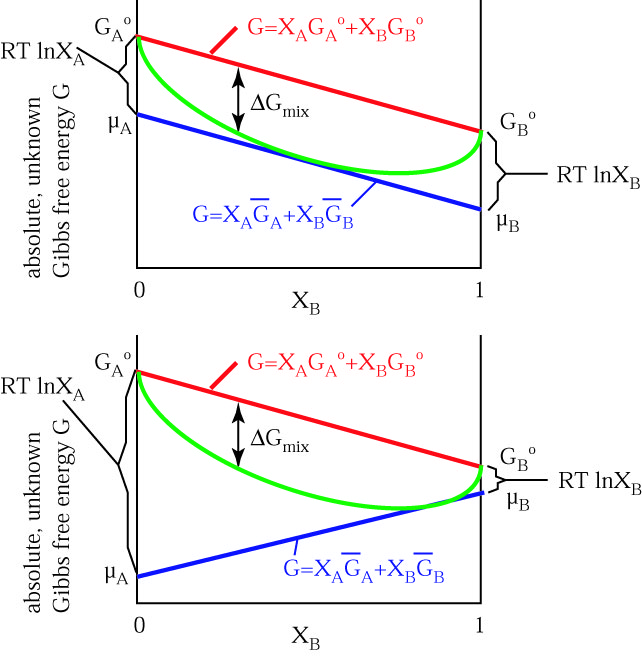
Based on the graphs, the activation energy is the height of the peaks, or the distance between the top of the curve and the reactants' free energy. The products have lower Gibbs free energy than the reactants. The molar gibbs free energy of a pure element is often give the symbol µ.
The theory proposed by R. This leads to a momentary increase in local energy, forming an intermediate (non-equilibrium) state, so-called transition (or activated) state. ∆G = ∆H - T∆Ssystem For any spontaneous change, ∆G will be negative.
The diagram above is a Gibbs-Free energy landscape/pathway, where the top of the diagram is the transition state between the substrate and the product. A measure of freedom of motion ΔGo = ΔHo - TΔSo ΔG,ΔH,ΔS, ΔE are state. O A, as it is equivalent to the chemical potential of the pure element.
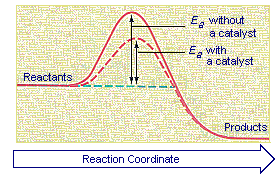
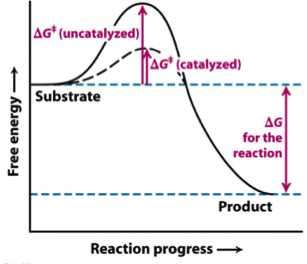
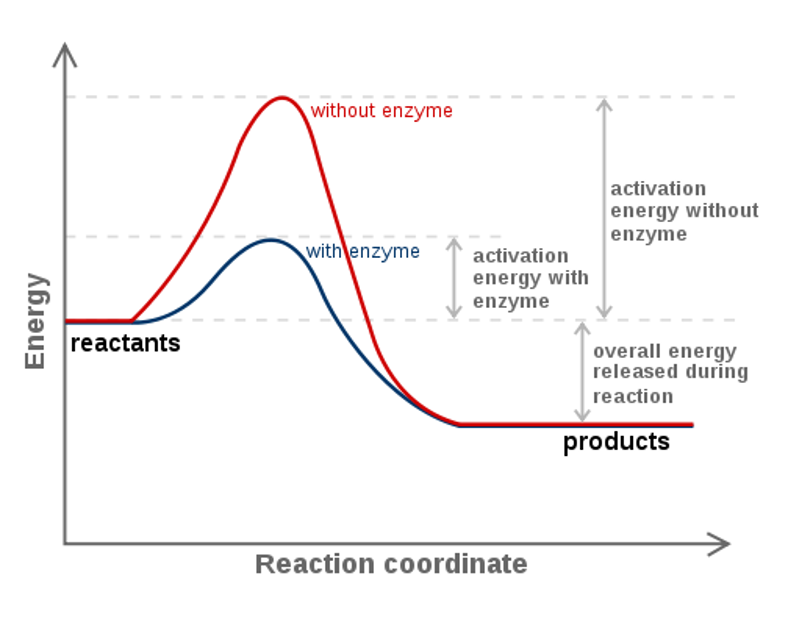
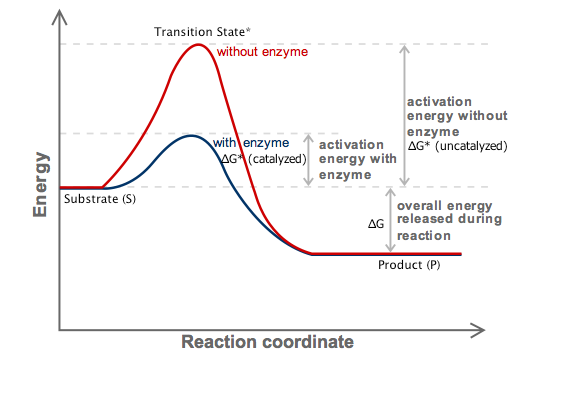
This tells us that the change in standard Gibbs Free Energy for the reaction (Δ G˚ rnx) is negative. Gibbs free energy (G) is also known as free energy or Gibbs energy. Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by stabilising the transition state, and in effect, lowers the activation energy (Ea) required.
Effect of Temperature on Gibbs Free Energy and Spontaneity of Reactions Chemistry Tutorial Key Concepts. Nodes in V are called variable nodes, nodes in F are called factor nodes. The Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) and how it's related to reaction spontaneity and equilibrium.
So they said, the change in Gibbs-free energy is equal to the change in enthalpy, or heat content, of a particular reaction minus the temperature of the reaction times the change in entropy, or broadly speaking randomness, between products and reactants in a particular reaction. The Gibbs free energy (also known as the Gibbs function) is defined as. In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that can be used to calculate the maximum of reversible work that may be performed by a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure.The Gibbs free energy (= −, measured in joules in SI) is the maximum amount of non-expansion work that can be extracted from a thermodynamically closed system (can exchange.
None of the above QUESTION 8 bets-sheet structure occurs when the two strands are oriented in. Generally, all reactions want to go to a lower energy state, thus a negative change is favored. The graph line's general trend is nearly horizontal.
The values of the rate constants, and hence Gibbs energies of @A@, depend upon the choice of concentration units (or of the thermodynamic @S@). G = H – T S (4-1). Activation energy is required for the reaction to proceed.
ΔG° = ΔH° - TΔS° ΔG° = -0.4 - 298(-0.2442) = -817.6 kJ mol-1. Ron Rusay" A Reaction Coordinate (Energy) Diagram Thermodynamic Quantities Gibbs standard free energy change (ΔGo) Enthalphy (ΔHo):. Ln(50) = (30)e-E a /(8.314)(679) E a = J/mol;.
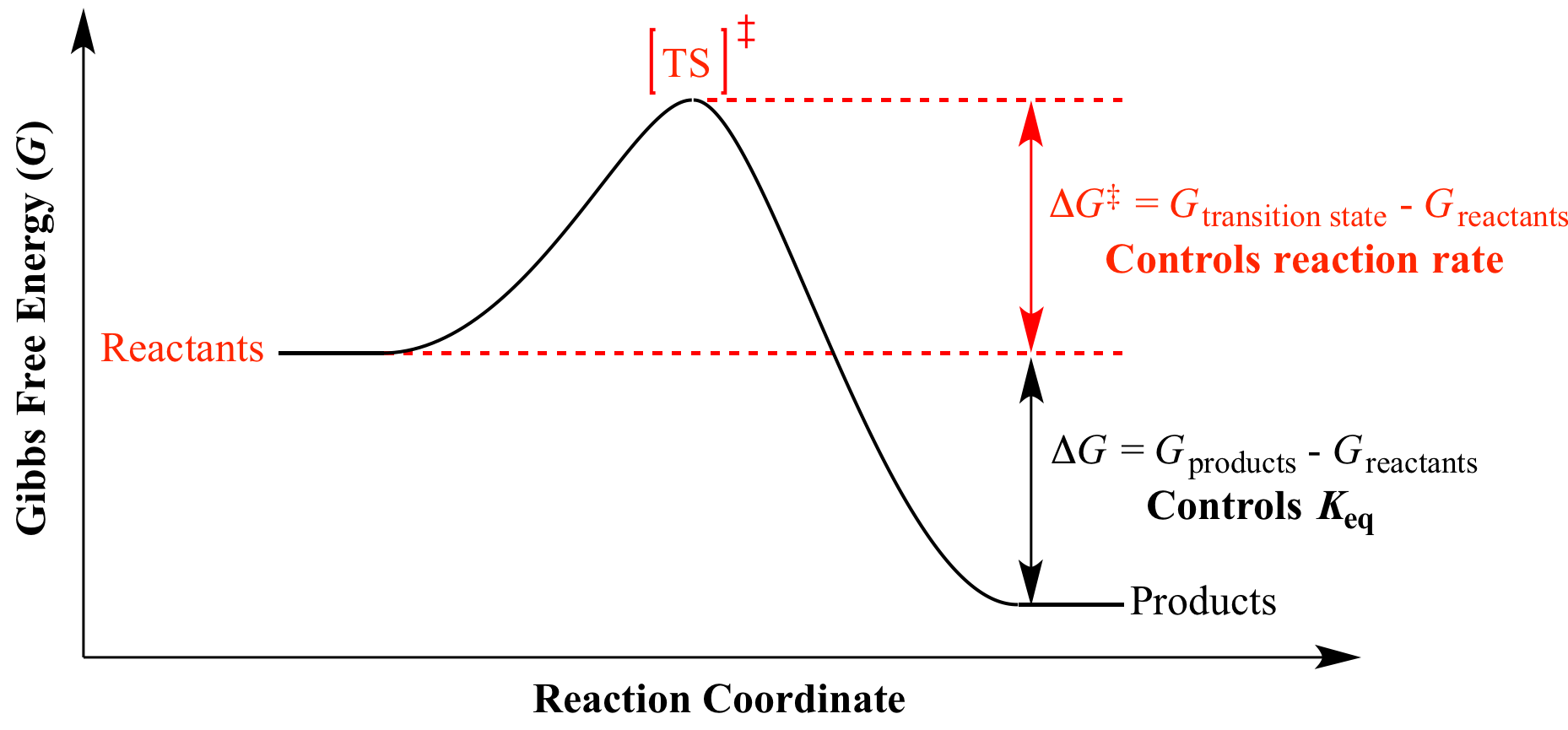
First, let’s review what this energy diagram tells us about the thermodynamics of the reaction illustrated by the energy diagram above. The overall change in G (Δ G) is the same in all three graphs. The superscript degree symbol (°) indicates that substances are in their standard states.
J/mol + (23 kJ/mol X 1000) = J/mol;. Then, for a unimolecular, one-step reaction, the approximate relationships Ea = Δ H‡ + RT and A = ( kBT / h) exp (1 + Δ S‡ / R) hold. Structural Biochemistry/Enzyme/Gibbs free energy graph.
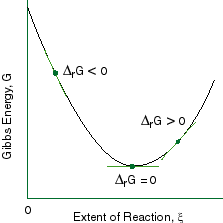
The entropy of the reaction d. If, however, the stability criteria are not satisfied for a multicomponent system phase transitions may occur. Delta G and the partial derivative of G with respect to xi are different quantities in spite of the fact that both are equal to delta Go + RTlnQ.
In other words, the reaction is. 50 45 40 35 B 30 E Standard Gibbs Free Energy, Gº (kJ) 25 15 А 10 5 0 Reaction Progress 2NH3 (g) 4 N2H4 (g) + H2 (9) 1. The limiting free energy density is given by the Bethe-approximation.
The law of mass action (24.7) does not allow to identify the reaction rate coefficients kb and kf individually, it only relates their ratio to the Gibbs free energy of reaction.We split the latter into two contributions, the Gibbs free energies of activation for backward and forward reactions, g¯b and g¯f , as where k0 is a dimensional factor. Enthalpy of activation, entropy of activation. Gibbs free energy c.
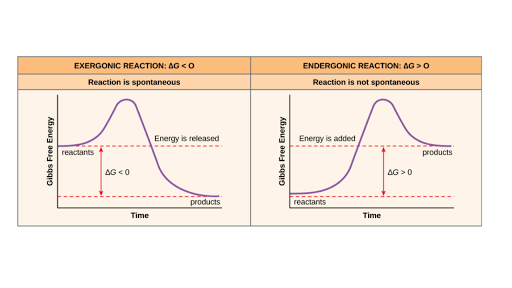
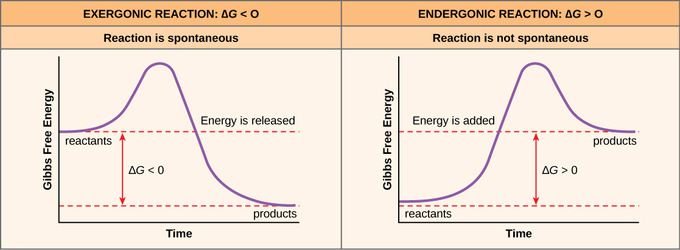
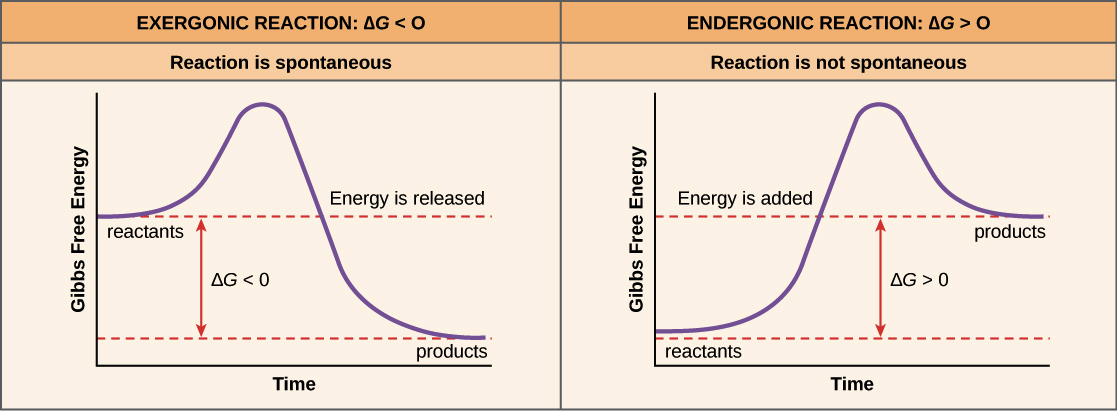
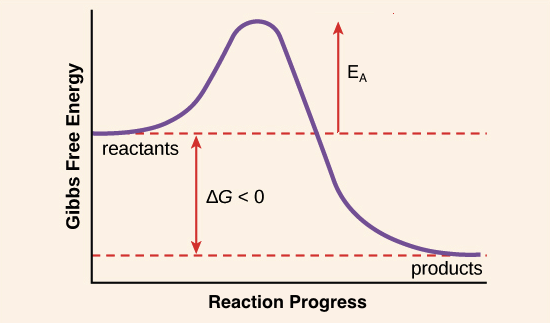
This is the currently selected item. Negative ΔG indicates that the reaction is exergonic and spontaneous. In Figure 1, energy refers to the free energy of the reaction (G).
O the difference between the product and the transition state. The change in entropy (S) increases. The thermodynamic potential for the Gibbs free energy is dG= SdT+VdP+ dN (1) If Pand Nare constant, we have @G @T P;N = S (2) If Tand Nare constant, we have @G @P T;N =V (3) We can use these derivatives to sketch qualitative graphs for Gas a func-tion of Pand Tfor water.
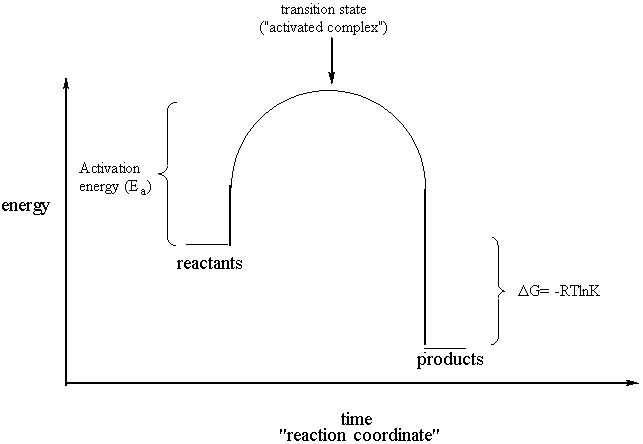
The change in the standard Gibbs Free Energy (G) of an exergonic reaction is negative (less than 0). A negative Gibbs free energy value indicates a spontaneous process and, in the reverse case, positive Gibbs free energy indicates non-spontaneity. ( gibz ), the Gibbs energy that must be added to that already possessed by a molecule or molecules to initiate a reaction.
A reaction can take place at standard-state conditions in. Gibbs energy of activation:. The free energy of the system decreases.
What we're going to do is we're just going to go with the highest activation energy so whichever one that is whether it's activation energy 1, 2, 3 or 10 let's say it's a 10-step or whatever you just go with the very highest activation energy and that is going to be your rate determining step, OK?. Gibbs free energy reaction coordinate profiles found in some textbooks. Exergonic reactions occur spontaneously (no outside energy is required to start.
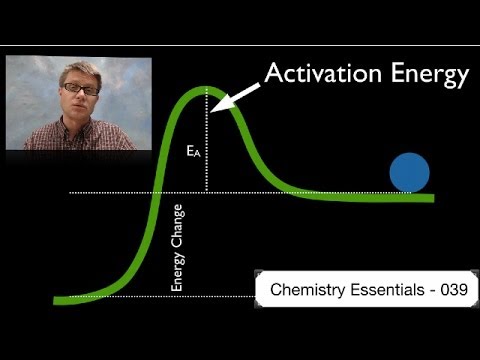
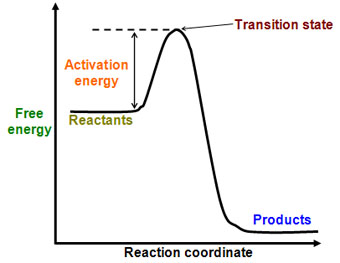
039 - Activation Energy In this video Paul Andersen explains how the activation energy is a measure of the amount of energy required for a chemical reaction. O b the difference between the substrste and the product. Use the equation \(\ln k = \ln A - \dfrac{E_a}{RT}\) to calculate the activation energy of the forward reaction.
The term standard state is used to describe a reference state for substances, and is a help in thermodynamical calculations (as enthalpy, entropy and Gibbs free energy calculations). Gibbs energy of activation (standard free energy of activation), \(\Delta ^{\ddagger}G^{\,\unicode{x26ac}}\). Gibbs Free Energy (G) is used to describe the useful energy in a reaction or the energy capable of doing work.
MS15a, Gibbs Free Energy and Phase Diagrams 11/00. Gibbs energy or Gibbs function ;. It shows a plane perpendicular to the axis of v (volume) and passing through point A - represents the initial state of the body.
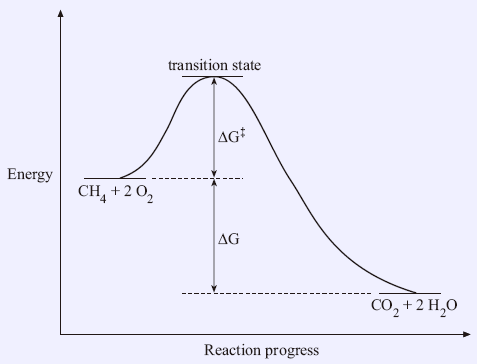
That is as a set of reactants go through the series of bond breaking and bond formation events, we see what happens to G as the molecules react. The excess molar volume, viscosity deviation and excess Gibbs free energy of activation of viscous flow have been investigated from the density and shear viscosity measurements of water–dioxane mixtures over the entire range of mole fractions from 293.15 to 309.15 K. The free energy of activation refers to the deltaG (Gibbs Free Energy) of the reaction.
.the difference between the substrste and the transition stste. As a function of composition, the gibbs free energy for the combination of pure A and pure B is a straight line connecting g. Endergonic, exergonic, exothermic, and endothermic.
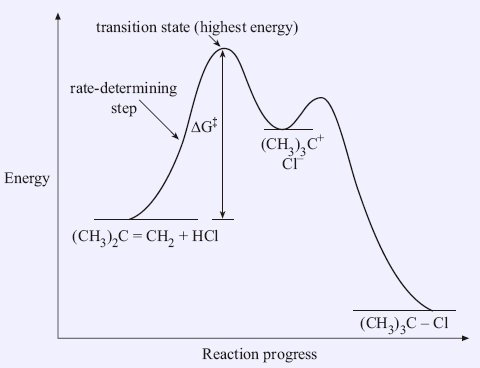
Activation energy is a term in the Arrhenius equation used to calculate the energy needed to overcome the transition state from reactants to products. The reason is that the reaction has a high activation. The energy diagram for a reaction model consisting of one enzyme, one substrate, and one product is depicted in many books where it is compared with that for the uncatalyzed reaction.
What is the activation energy, Ea, of this reaction?. Qε and Qη are sections of the planes η = 0 and ε = 0, and therefore parallel to the axes of ε (internal energy) and η (entropy), respectively. The reaction always occurs quickly.
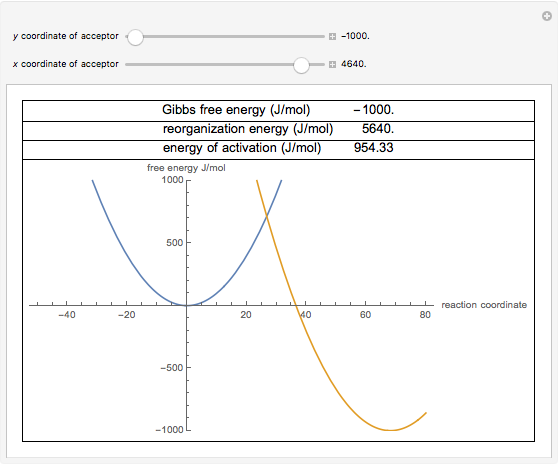
The energy level of the products is lower than that of the reactants. The sign of the change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG) for a chemical reaction tells us if the reaction is spontaneous or not:. Marcus in 1956 1–3 provides a method to calculate the activation energy of a reaction by using a parabolic model to calculate activation energy.
For any chemical reaction, regardless of how negative the actual change of Gibbs free energy (ΔG) is, the reactants must overcome a kinetic barrier to proceed with the conversion to products.According to the transition state theory, this barrier is called the Gibbs free activation energy (ΔG ≠).The reaction rate is a negative exponential function of this parameter. We can graph two parabolas as a simplified representation of reactant and product energy surfaces then numerically obtain values for reorganization energy and change in Gibbs free energy from the graphical model. A large girth sequence of (d,k)-biregular factor graphs, then the free energy density of Gn converges.
The amount of energy obtained from the breakdown of a larger, more structured molecule, and available to build large, structured molecules from smaller, less complex ones (or power muscles or other contractile processes) is known as "Gibbs' Free Energy", G. In which S refers to the entropy of the system.Since H, T and S are all state functions, so is G.Thus for any change in state, we can write the extremely important relation. (ΔH°, ΔG°, S°) Definitions of standard states:.
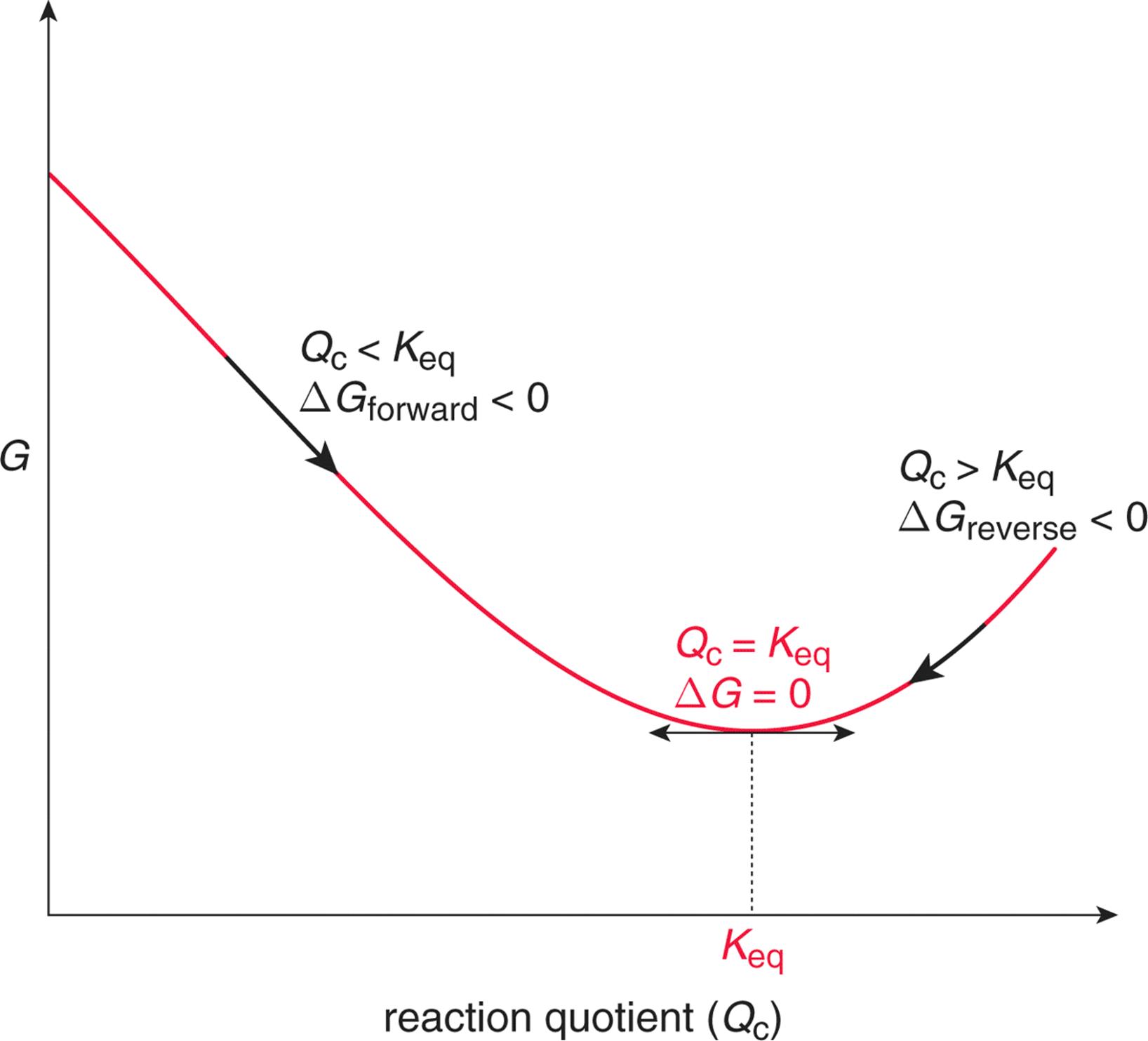
Fix two integers d,k≥ 2. The equilibrium constant is the something like this:. How does this simple equation encompass the entropy change of the world ΔS total.
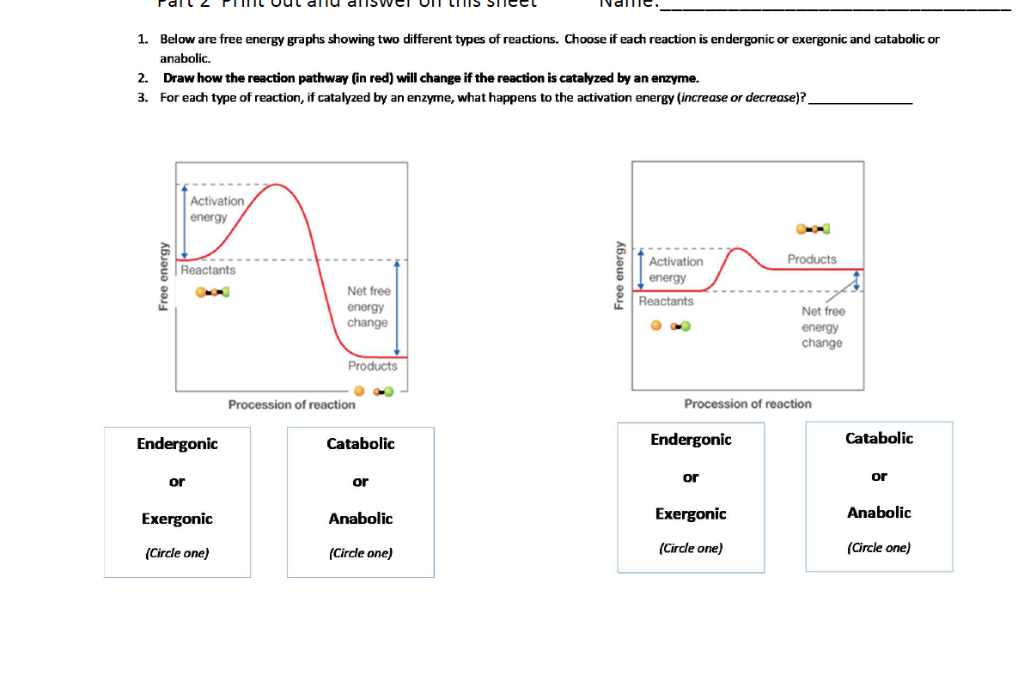
The method for constructing such graphs is explained. The highest activation energy is therefore the highest peak. The Gibbs free energy graph shows whether or not a reaction is spontaneous-- whether it is exergonic or endergonic.
Also known as free enthalpy 1 to distinguish it from Helmholtz free energy) is a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" or process-initiating work obtainable from a. Free energy is the component of the total energy of a system that is available to do work at constant temperature and pressure and is represented by the symbol G. The graph line's general trend is increasing from left to right.
ΔG is the overall energy released during the reaction and accounts for the equilibrium of the reaction. ΔG = ΔH – T ΔS (4-2) Must know this!. At equilibrium all potentials, the internal energy, the enthalpy, the Gibbs free energy, and the Helmholtz free energy are convex functions of the mole fractions.
It is easy as long as you remember to convert the entropy change value into kJ. The heat given off or absorbed during a reaction Entropy (ΔSo):. This is a Gibbs free energy graph by Josiah Willard Gibbs.
Δ G‡ = Δ H‡ – T Δ S‡. Enzymes are catalysts that lower a reactions activation energy (Ea), and thus increases the rate of the reaction. Gibbs free energy specifically refers to the energy associated with a chemical reaction that is available after accounting for entropy.
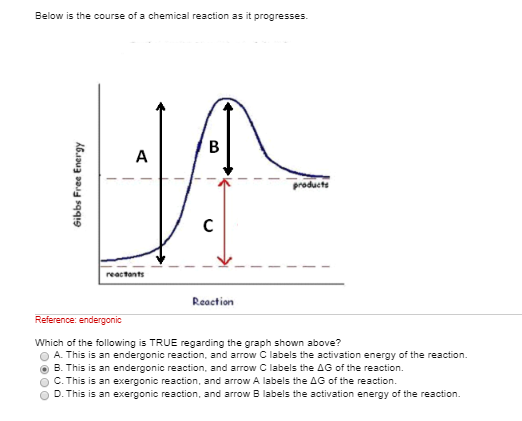
If you know the activation energy of all the steps of the catalyzed reaction, and you know by how much the activation energy (E a) of your first step is increased, then you may infer your k cat. Which letter(s) on the graph represent(s) the reaction transition state(s)?. Every chemical reaction involves a change in free energy, called delta G (∆G).
The Activation Energy Of Chemical Reactions
Notes Week 2 1 Goes Over Glycolysis The Krebs Cycle Oxidative Phosphorylation The Light Studocu

Energy And Enzymes Biological Principles
Gibbs Free Energy Graph Activation Energy のギャラリー
Www Eng Utah Edu Lzang Images Lecture 1 Pdf
Transition States And Activation Energy Open Textbooks For Hong Kong
Solved 1 Below Are Free Energy Graphs Showing Two Differ Chegg Com
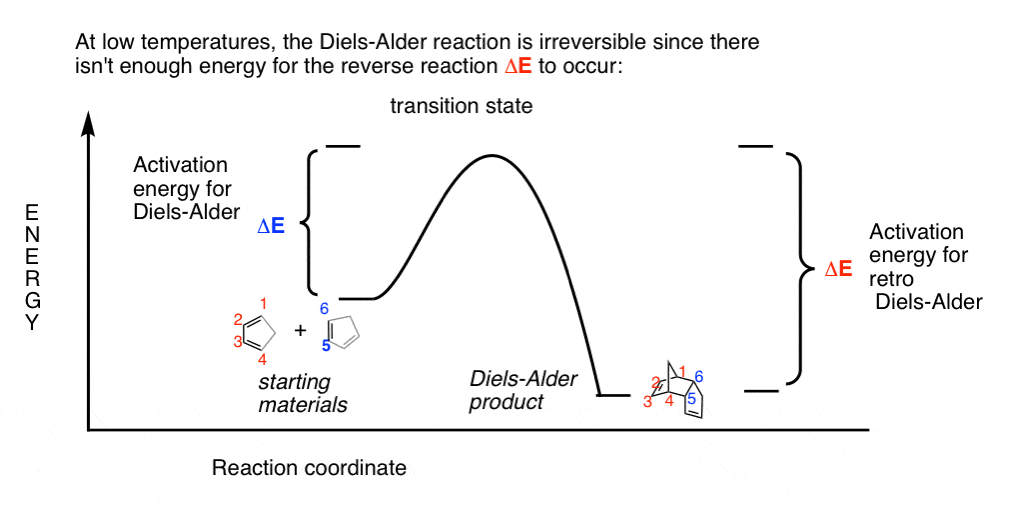
Kinetic And Thermodynamic Control In The Diels Alder Reaction
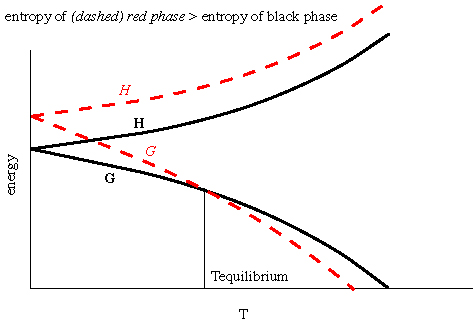
Thermodynamics Notes
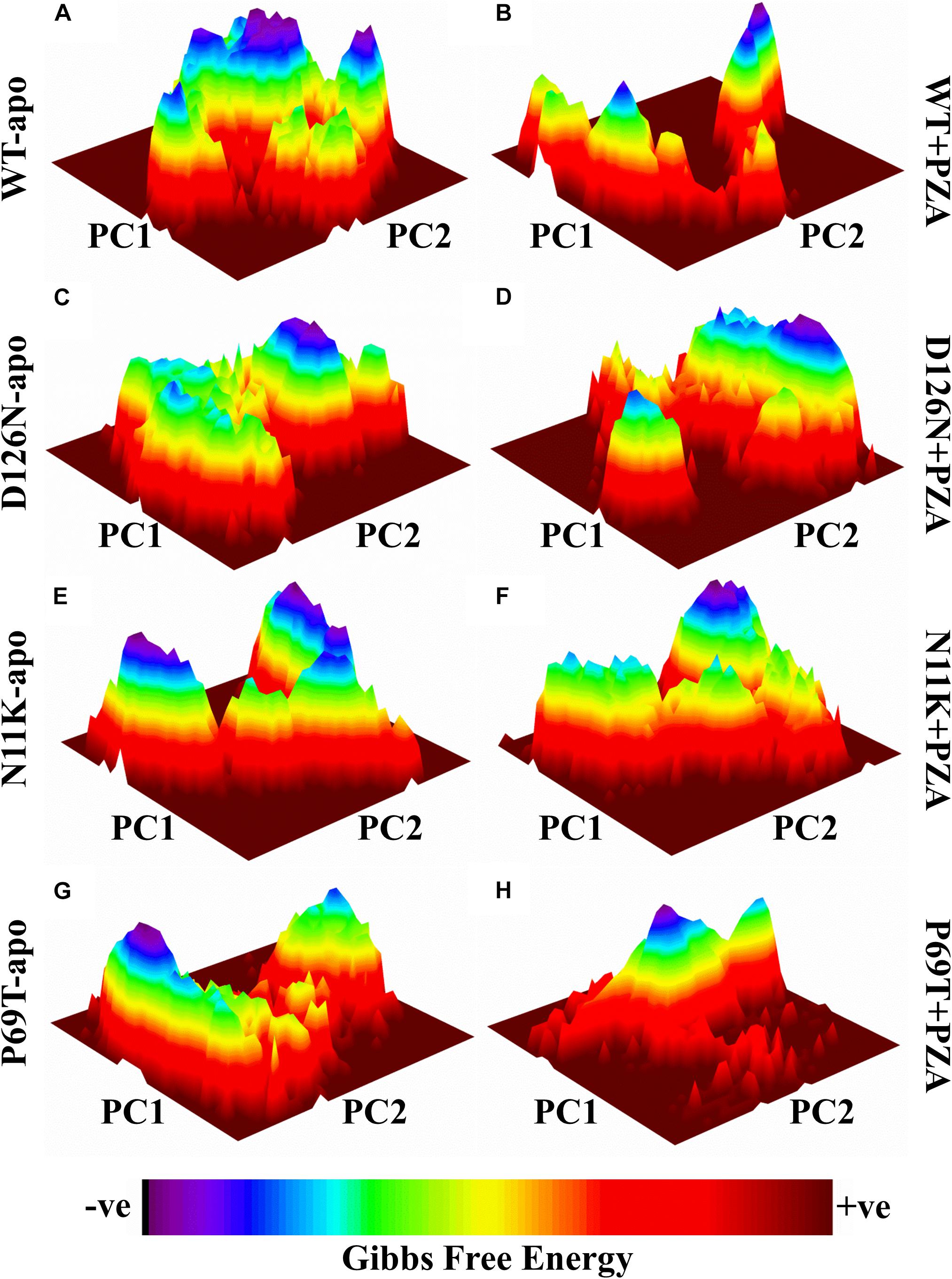
Frontiers Gibbs Free Energy Calculation Of Mutation In Pnca And Rpsa Associated With Pyrazinamide Resistance Molecular Biosciences
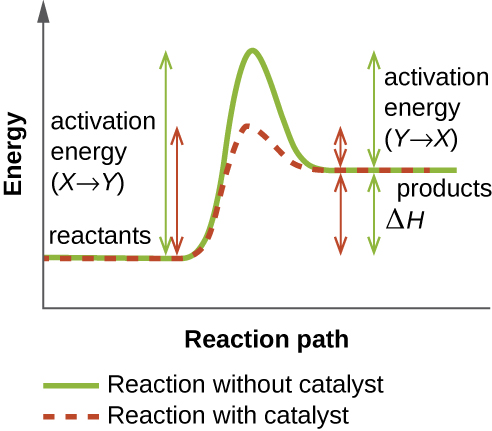
8 1 Energy Redox Reactions And Enzymes Microbiology Canadian Edition
Thermodynamics Notes

Enzymes Biology For Non Majors I
How To Interpret Thermodynamics Of Reactions Organic Chemistry Help

What Is The Effect Of Using Catalyst In A Reaction On I Activation Energy Ii Gibbs Energy Of A Reaction Chemistry Chemical Kinetics Meritnation Com
Www Theexpertta Com Book Files Openstaxbio2e Chapter 6 metabolism Pdf
Gibbs Free Energy Thermochemistry Training Mcat General Chemistry Review

Solution The Diagram Below Represents A S Clutch Prep
Http People Uleth Ca Steven Mosimann hm3300 hm3300 L3 Pdf

Structural Biochemistry Endergonic Reaction Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World

Enzyme Kinetics What Happens At The Peak Of The Gibbs Energy Graph Biology Stack Exchange

Exploring The Sulfatase 1 Catch Bond Free Energy Landscape Using Jarzynski S Equality Scientific Reports
Free Energy Endergonic Vs Exergonic Reactions Article Khan Academy
What Describes The Change In Gibbs Free Energy G Of A Spontaneous Reaction

Energy And Enzymes Biological Principles

Activation Energy Bioninja
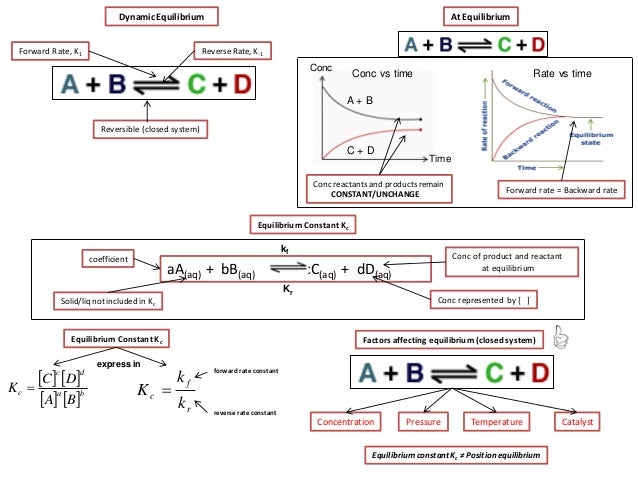
Ib Chemistry On Gibbs Free Energy And Equilibrium Constant Kc
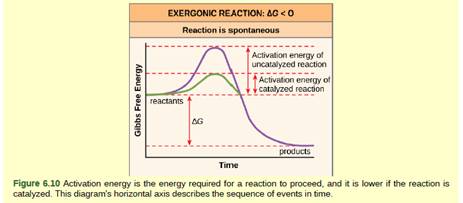
Figure 6 10 If No Activation Energy Were Required To Break Down Sucrose Table Sugar Would You Be Able To Store It In A Sugar Bowl Bartleby

Advanced Mathematical Research Author Md Tauseef Ibrahim Abraham Malik Thermodynamics Chemical Kinetics Rate Constant Free Energy Of Formation Effect Of Temperature On Spontaneity Thermodynamics In Biological Systems Atp Coupled Reactions
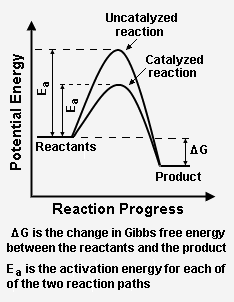
Catalysis Knowino

The Combined Effects Of Reactant Kinetics And Enzyme Stability Explain The Temperature Dependence Of Metabolic Rates Delong 17 Ecology And Evolution Wiley Online Library

Free Energy And Chemical Reactions Ppt Download
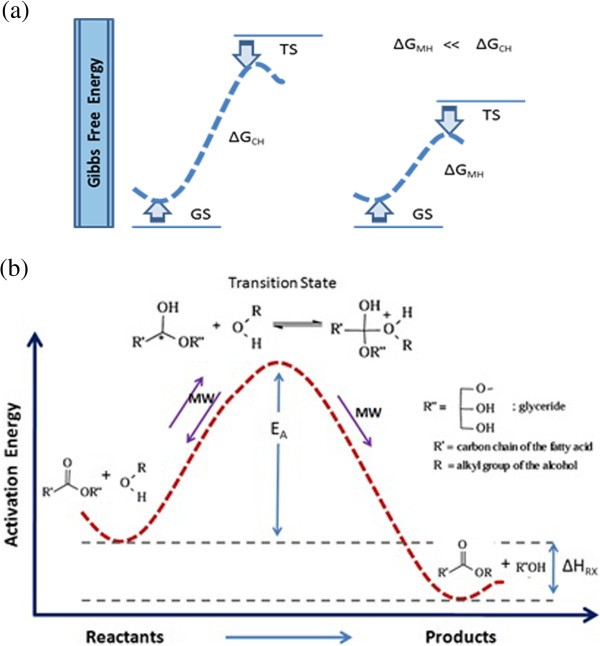
Figure 6 Microwave Energy Potential For Biodiesel Production Springerlink

Quia Ap Chapter 8 An Introduction To Metabolism Detailed
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/endergonic-vs-exergonic-609258_final-2904b2c359574dfcb65a9fca2d54179a.png)
Endergonic Vs Exergonic Reactions And Processes

Kinetics Teach That Electronic Coupling Lowers The Free Energy Change That Accompanies Electron Transfer Pnas
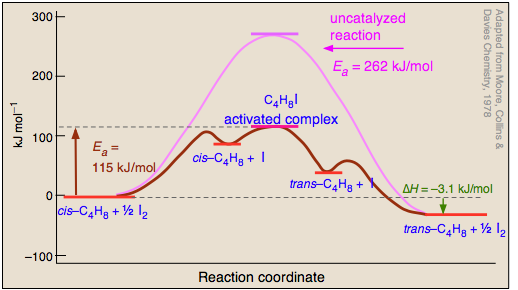
6 2 3 3 The Arrhenius Law Activation Energies Chemistry Libretexts
6 2 3 3 The Arrhenius Law Activation Energies Chemistry Libretexts

Gibbs Free Energy Of Activation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
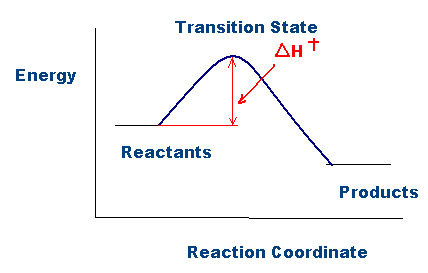
Free Energy The School Of Biomedical Sciences Wiki
Dc Etsu Edu Cgi Viewcontent Cgi Article 4859 Context Etd
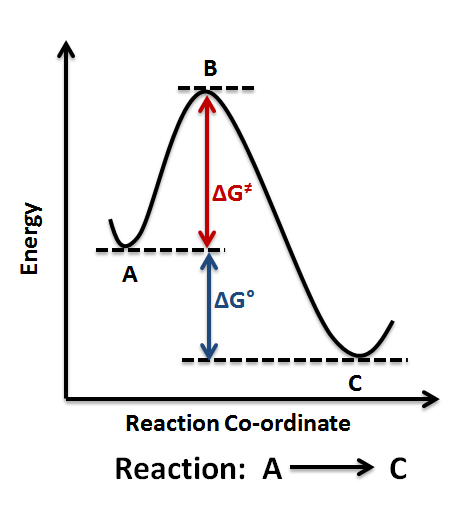
Energy Profile Chemistry Wikipedia

Enzymes Effect On Activation Energy And Free Energy Youtube

Mcat Diagram Quizlet

Enthalpy Entropy And Gibbs Free Energy Ppt Video Online Download

260h Licensed For Non Commercial Use Only 12 Reaction Dynamics

Activation Energy And Temperature Dependence Boundless Chemistry
Activation Of Reactions Gibbs Free Energy Of Activation Hvac Machinery
Concepts In Biochemistry Concept Reviews

Reaction Coordinate Wikipedia

Gibbs Free Energy In Reaction Profiles Chemistry Community
Structural Biochemistry Enzyme Gibbs Free Energy Graph Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World

Enzymes Openstax Biology
Solved Below Is The Course Of A Chemical Reaction As It P Chegg Com
Solved The Gibbs Free Energy Of Activation Dg Delta G Chegg Com
Free Energy Endergonic Vs Exergonic Reactions Article Khan Academy
Bond Strain Creative Enzymes

Homogeneous Nucleation Tec Science

Chapter 8 Enzymes

Enzyme Powerpoint Slides
Energy Diagram Module Series Part Two Gibbs Free Energy And Spontaneity Organic Chemistry Help

Effect Of The Catalysts In A Thermodynamically Favourable Reaction Download Scientific Diagram
Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Dg
If A Catalyst Lowers Activation Energy By Equal Amounts For Both The Forward And Reverse Reaction Shouldn T The Equilibrium Be Changed As According To The Maxwell Curve The Ratio Of Particle With

Activation Energy Bioninja
Activation Energy Youtube
Activation Energy Article Enzymes Khan Academy
Http Sites Fas Harvard Edu Lsci1a 11 9notes Pdf
Chapter 9 Lecture Notes

Best Lesson 2 Enzymes Flashcards Quizlet

Endergonic Vs Exergonic Reactions And Examples

2 3 3 Potential Kinetic Free And Activation Energy
Pdfs Semanticscholar Org 95ce D978a5e1b65fb9b564dbca0dec26a8c5 Pdf

Team Kuleuven Thermodynamics 11 Igem Org

Arrhenius And Activation Energy Plots For The Respiration Rate Of Download Scientific Diagram
Transition States And Activation Energy Open Textbooks For Hong Kong

What Do We Mean When We Talk About Gibbs Free Energy Physics Stack Exchange
Ch103 Chapter 7 Chemical Reactions In Biological Systems Chemistry
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqsihy1k7c Quvudtb9wir3b97dngimkhlpgltoicxluiykgzl7 Usqp Cau

Transition State And Free Energy Chemistry Stack Exchange
Chapter 8 Welcome To Ap Biology

Question F54 Socratic

Energy And Enzymes
Marcus Theory Of Electron Transfer Reactions Wolfram Demonstrations Project

Homogeneous Nucleation Tec Science
15 2 Entropy And Spontaneity Ib Alchemy
Entropy Free Full Text Chemical Reaction Networks Possess Intrinsic Temperature Dependent Functionality Html

Organic Chemistry I Ii Reading Assignment Chemical Reactivity And Mechanisms Top Hat
6 1 Activation Energy Sl Youtube
Thermodynamics And Kinetics
How Do Enzymes Affect Gibbs Free Energy Socratic

Plot Of Linear Form For Activation Energy And Gibbs Free Energy At Download Scientific Diagram
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrors0filkikzl3hc Jw13crx7dzxavkb8klbg V C4kq2wosqf Usqp Cau
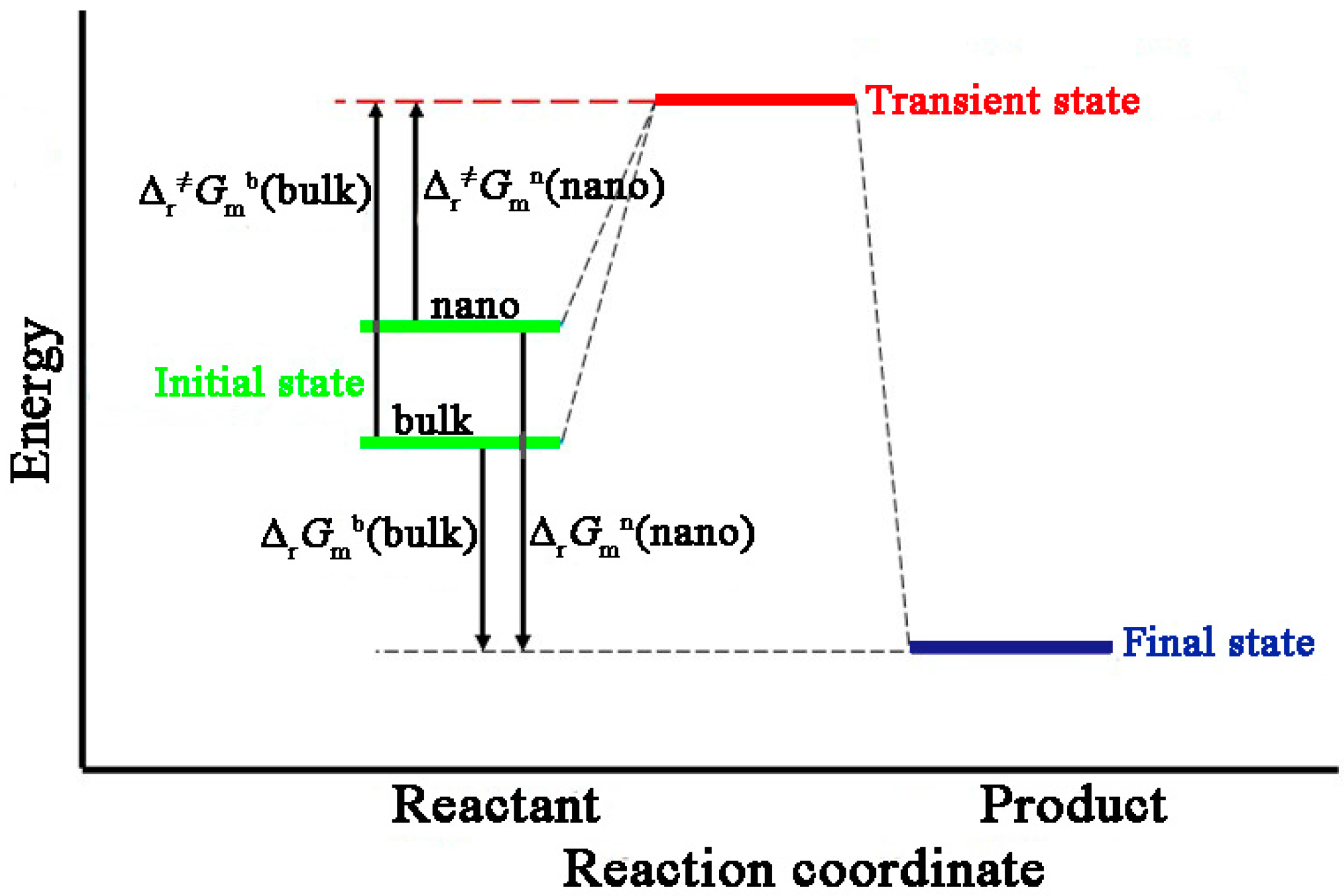
Entropy Free Full Text Reaction Kinetic Parameters And Surface Thermodynamic Properties Of Cu2o Nanocubes Html
Q Tbn 3aand9gctrsl31jde5uczcz7pbe2gmdftgonasq3ewasam2kf1iwmd B Usqp Cau
6 2 3 3 The Arrhenius Law Activation Energies Chemistry Libretexts
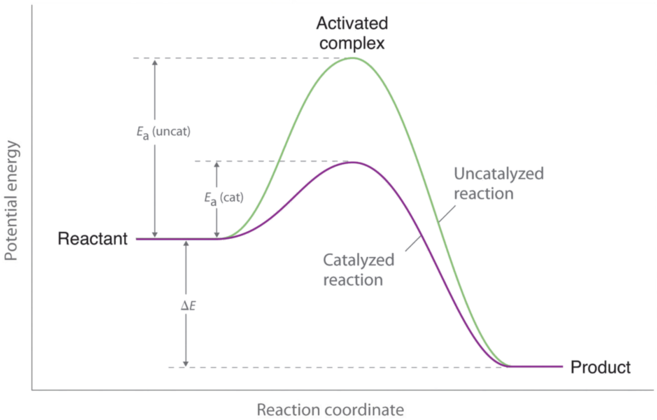
6 2 3 3 The Arrhenius Law Activation Energies Chemistry Libretexts
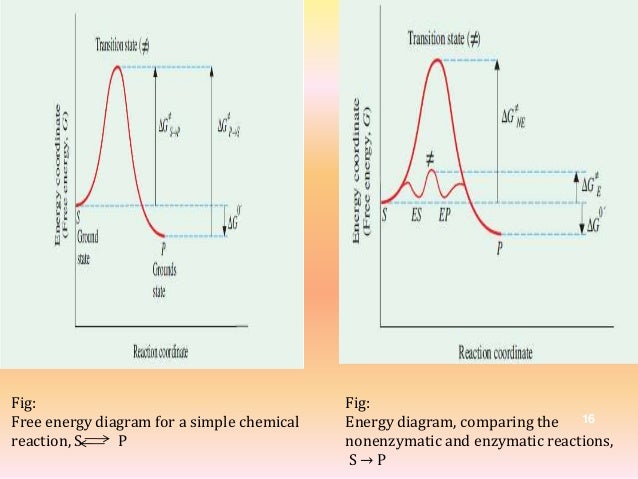
Enzyme Inhibitors Activation Energy And Mec

Solvent Selection For Chemical Reactions Automated Computational Screening Of Solvents Using The Smd Model
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqzes7gptz6xko8eew2ewqbd1wkdjh8fhcmtbb1pbr5vh6zqgqg Usqp Cau
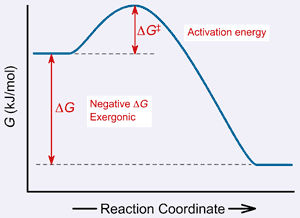
Thermodynamics
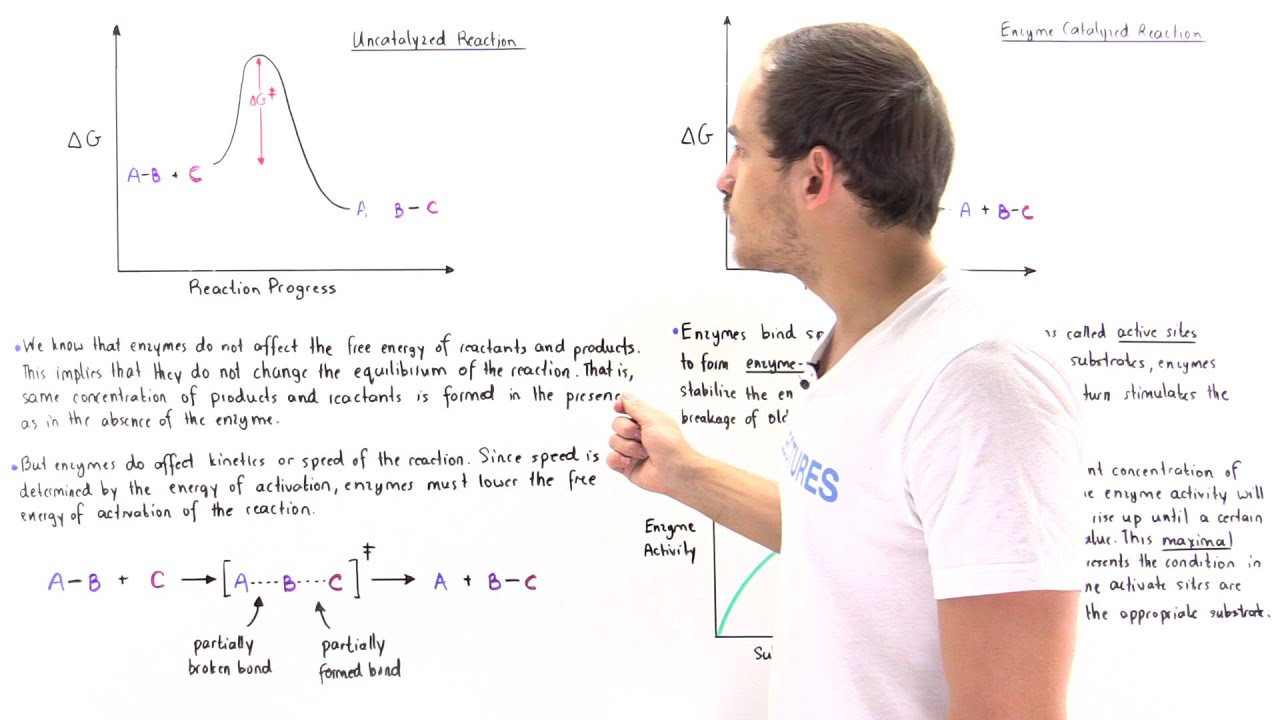
Ak Lectures Enzymes Effect On Activation Energy And Free Energy

260h Licensed For Non Commercial Use Only Reaction Dynamics

Introduction To The Transition State Theory Intechopen

Activation Energy Wikipedia



